Summary
This report analyses the read counts of the Del and Het samples only. The report begins with some general Setup and is followed by various analyses denoted by a prefix (y, ym, yf):
y: Analysis of aggregated technical replicates with Remove Unwanted Variation (RUV) normalizationym: Male-only: analysis of aggregated technical replicates using RUV normalizationyf: Female-only: analysis of aggregated technical replicates using RUV normalization
Setup
Load data
Show code
sce <- readRDS(here("data", "SCEs", "C086_Kinkel.preprocessed.SCE.rds"))
# NOTE: Reorder samples for plots (e.g., RLE plots).
sce <- sce[, order(sce$smchd1_genotype_updated, sce$sex, sce$mouse_number)]
# Restrict analysis to read counts
assays(sce) <- list(counts = assay(sce, "read_counts"))
outdir <- here("output", "DEGs", "reads")
dir.create(outdir, recursive = TRUE)
Gene filtering
We filter the genes to only retain protein coding genes.
Sample filtering
We filter out the WT samples as these are not useful for DE analysis since there is only 1 biological replicate.
Show code
sce <- sce[, sce$smchd1_genotype_updated != "WT"]
Show code
colData(sce) <- droplevels(colData(sce))
# Some useful colours
sex_colours <- setNames(
unique(sce$sex_colours),
unique(names(sce$sex_colours)))
smchd1_genotype_updated_colours <- setNames(
unique(sce$smchd1_genotype_updated_colours),
unique(names(sce$smchd1_genotype_updated_colours)))
mouse_number_colours <- setNames(
unique(sce$mouse_number_colours),
unique(names(sce$mouse_number_colours)))
Create DGEList objects
Show code
y <- sumTechReps(x, x$samples$genotype.mouse)
ym <- y[, y$samples$sex == "M"]
yf <- y[, y$samples$sex == "F"]
Gene filtering
For each analysis, shown are the number of genes that have sufficient counts to test for DE (TRUE) or not (FALSE).
y
Show code
y_keep_exprs <- filterByExpr(y, group = y$samples$group, min.count = 5)
y <- y[y_keep_exprs, , keep.lib.sizes = FALSE]
table(y_keep_exprs)
y_keep_exprs
FALSE TRUE
3040 11450 ym
Show code
ym_keep_exprs <- filterByExpr(ym, group = ym$samples$group, min.count = 5)
ym <- ym[ym_keep_exprs, , keep.lib.sizes = FALSE]
table(ym_keep_exprs)
ym_keep_exprs
FALSE TRUE
2891 11599 yf
Show code
yf_keep_exprs <- filterByExpr(yf, group = yf$samples$group, min.count = 5)
yf <- yf[yf_keep_exprs, , keep.lib.sizes = FALSE]
table(yf_keep_exprs)
yf_keep_exprs
FALSE TRUE
2977 11513 Normalization
Normalization with upper-quartile (UQ) normalization.
Show code
x <- calcNormFactors(x, method = "upperquartile")
y <- calcNormFactors(y, method = "upperquartile")
ym <- calcNormFactors(ym, method = "upperquartile")
yf <- calcNormFactors(yf, method = "upperquartile")
Aggregation of technical replicates
We have up to 3 technical replicates from each biological replicate. Ideally, the technical replicates are very similar to one another when view on an MDS plot. However, Figure 1 shows that:
- Some of the technical replicates are more variable than we would like
- Those ‘outlier’ samples have smaller library sizes
Show code
x_mds <- plotMDS(x, plot = FALSE)
x_df <- cbind(data.frame(x = x_mds$x, y = x_mds$y), x$samples)
rownames(x_df) <- colnames(x)
p1 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = smchd1_genotype_updated, label = rownames(x_df)),
data = x_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = smchd1_genotype_updated_colours)
p2 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = sex, label = rownames(x_df)),
data = x_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = sex_colours)
p3 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = mouse_number, label = rownames(x_df)),
data = x_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = mouse_number_colours)
p4 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = log10(lib.size), label = rownames(x_df)),
data = x_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
scale_colour_viridis_c() +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2")
p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + plot_layout(ncol = 2)
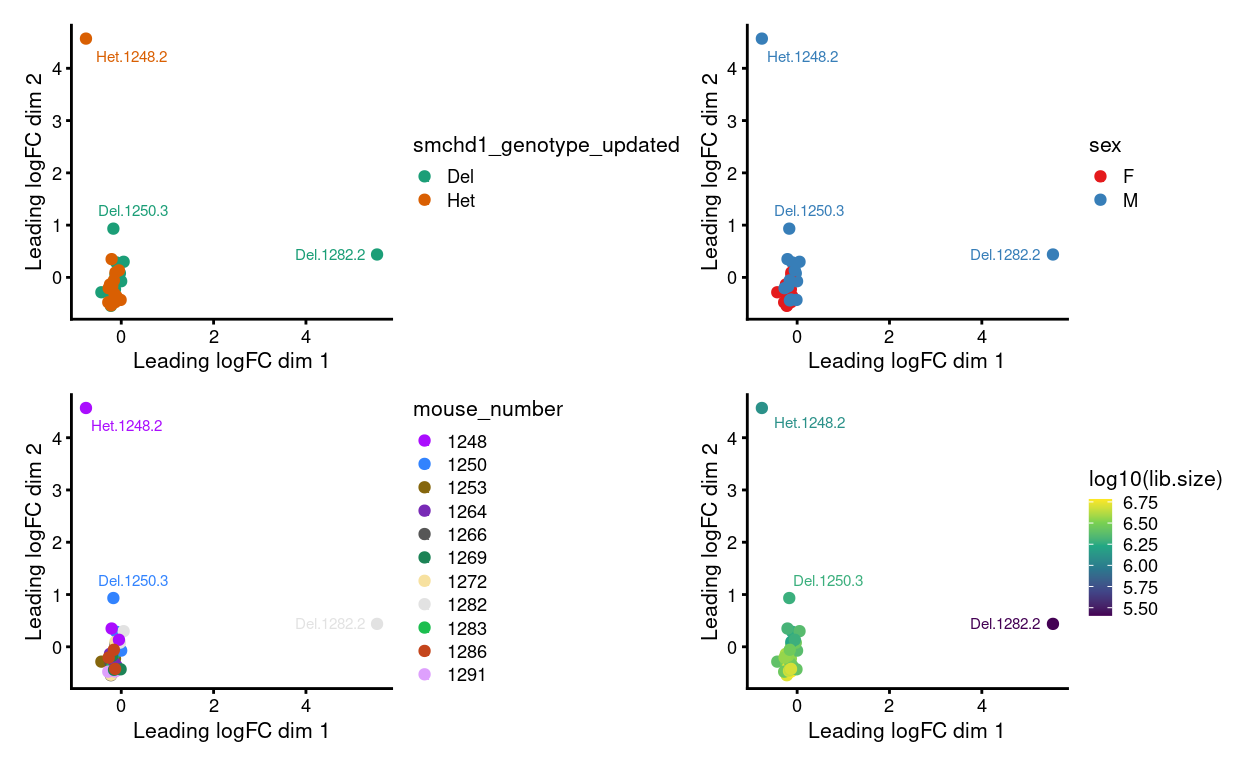
Figure 1: MDS plots of individual technical replicates coloured by various experimental factors.
Although we could analyse the data at the level of technical replicates, this is more complicated. It will make our life easier by aggregating these technical replicates so that we have 1 sample per biological replicate. To aggregate technical replicates we simply sum their counts.
Figure 2 shows the MDS plot after aggregating the technical replicates. We still observe that:
- Samples cluster more strongly by sex than by genotype
- Some of the variation is associated with library size
These observations (and others) prompt us to consider further normalization of the data.
Show code
y_mds <- plotMDS(y, plot = FALSE)
y_df <- cbind(data.frame(x = y_mds$x, y = y_mds$y), y$samples)
rownames(y_df) <- colnames(y)
p1 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = smchd1_genotype_updated, label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = smchd1_genotype_updated_colours)
p2 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = sex, label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = sex_colours)
p3 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = mouse_number, label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = mouse_number_colours)
p4 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = log10(lib.size), label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
scale_colour_viridis_c() +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2")
p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + plot_layout(ncol = 2)
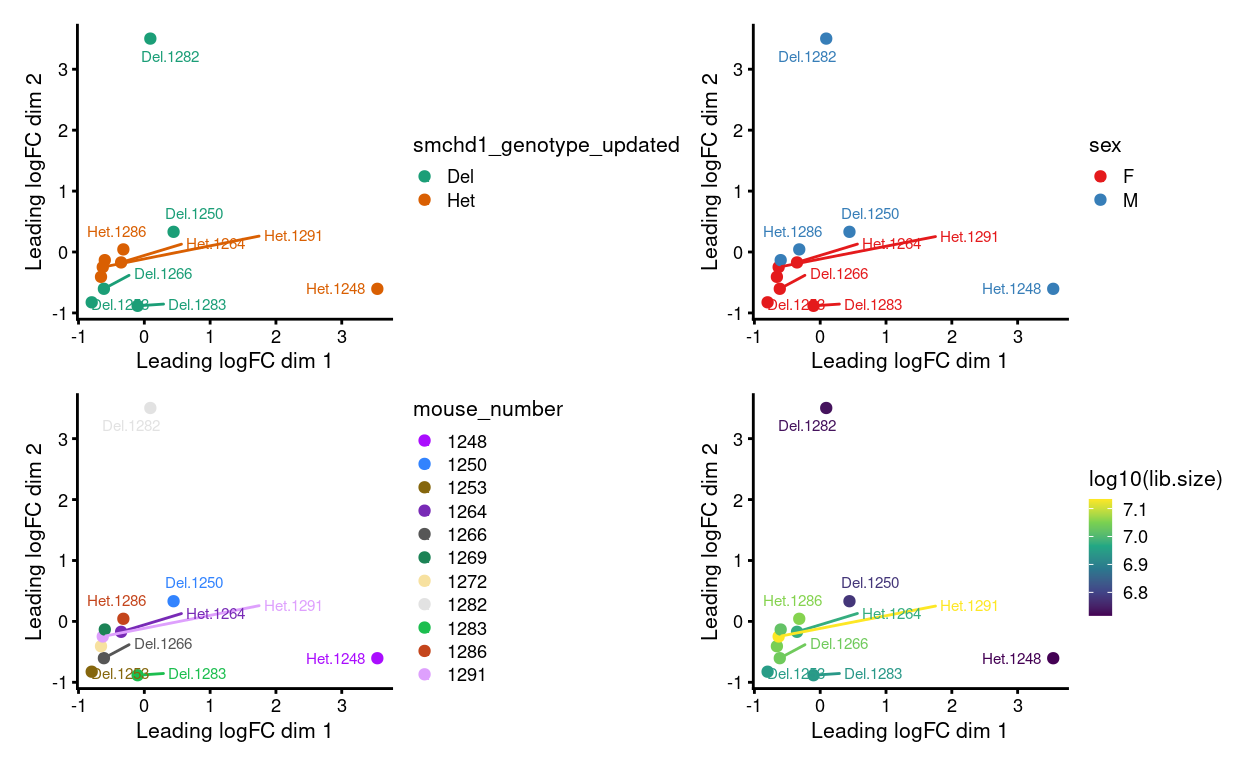
Figure 2: MDS plots of aggregated technical replicates coloured by various experimental factors.
Further normalization
Show code
design <- model.matrix(
~0 + smchd1_genotype_updated + sex,
y$samples)
colnames(design) <- sub(
"smchd1_genotype_updated|sex",
"",
colnames(design))
y <- estimateDisp(y, design)
dgeglm <- glmFit(y, design)
contrasts <- makeContrasts(Del - Het, levels = design)
dgelrt <- glmLRT(dgeglm, contrast = contrasts)
tt <- topTags(dgelrt, n = Inf)
summary(decideTests(dgelrt))
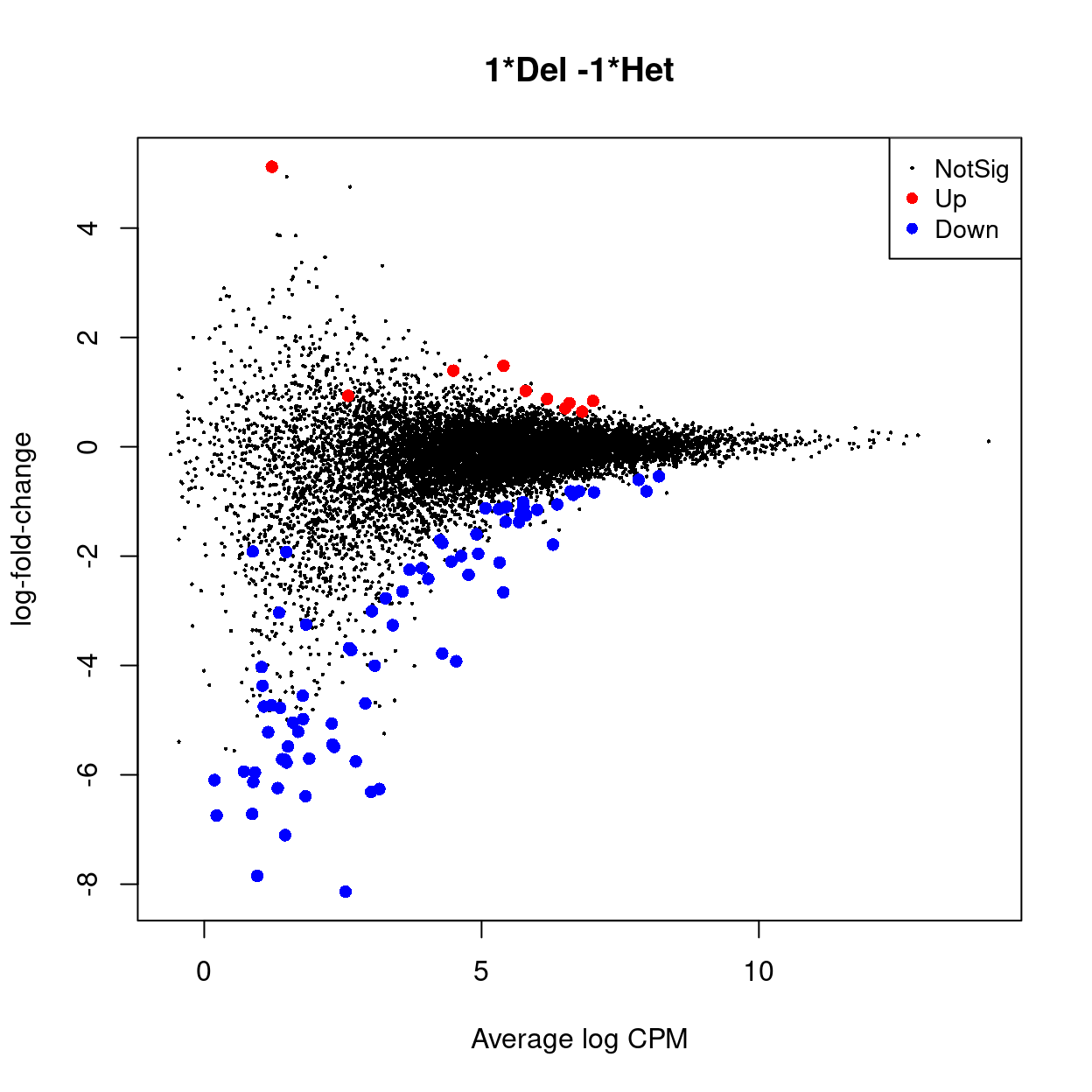
The MDS plots in Figure 2 strongly suggest that we will not detect many differentially expressed genes (DEGs) using a standard analysis. This is borne out in Figure 3, which shows the results of a standard edgeR analysis of the data (there is 3 DEG (\(FDR < 0.05\))).
Show code
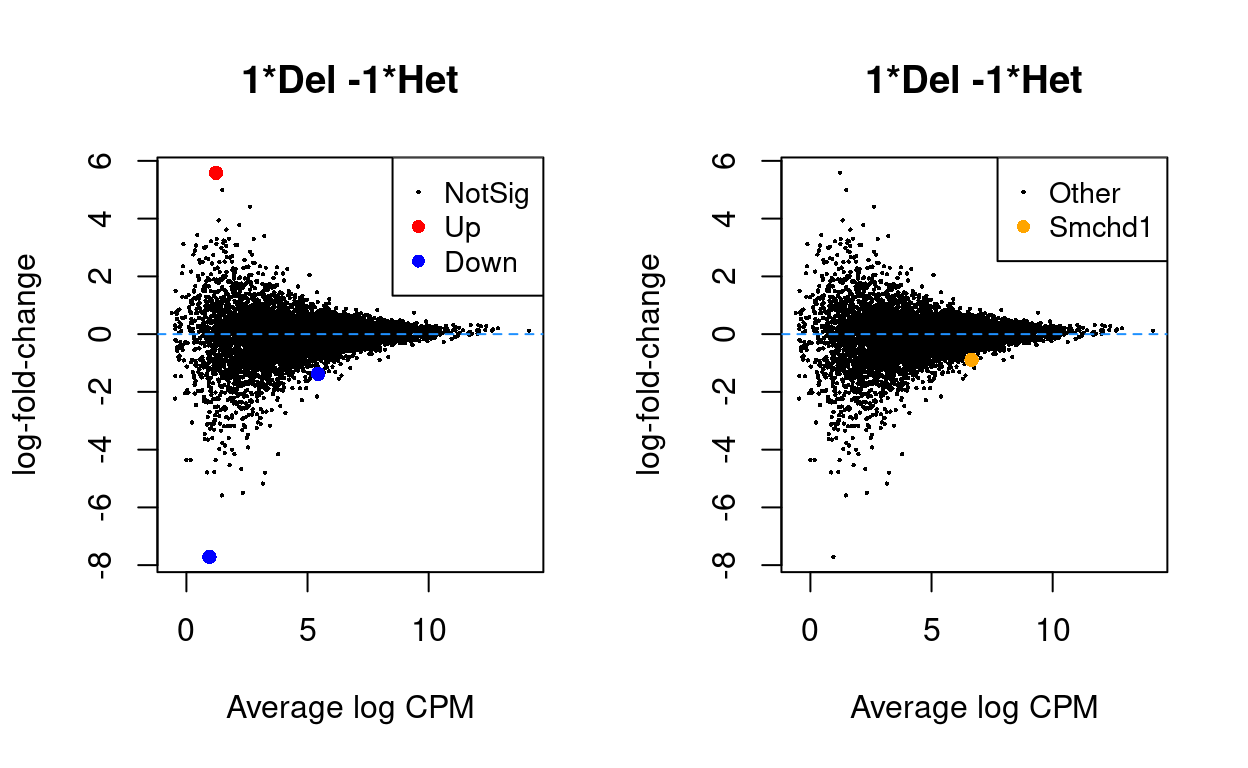
Figure 3: MD plot highlighting DE genes (left) and Smchd1 (right).
To further normalize the data, we use RUVs.
Show code
differences <- makeGroups(
interaction(y$samples$smchd1_genotype_updated, y$samples$sex))
ruv <- RUVs(
x = betweenLaneNormalization(y$counts, "upper"),
cIdx = rownames(y),
k = 3,
scIdx = differences)
design <- model.matrix(
~0 + smchd1_genotype_updated + sex + ruv$W,
y$samples)
colnames(design) <- sub(
"ruv\\$|smchd1_genotype_updated|sex",
"",
colnames(design))
Figure 4 shows that after applying RUVs samples cluster by combination of genotype and sex, which is what we want to see.
Therefore, we opt to further normalize the data using RUVs in each DE analysis1
Show code
y_mds <- plotMDS(cpm(ruv$normalizedCounts, log = TRUE), plot = FALSE)
y_df <- cbind(data.frame(x = y_mds$x, y = y_mds$y), y$samples)
rownames(y_df) <- colnames(y)
p1 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = smchd1_genotype_updated, label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = smchd1_genotype_updated_colours)
p2 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = sex, label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = sex_colours)
p3 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = mouse_number, label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = mouse_number_colours)
p4 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = log10(lib.size), label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
scale_colour_viridis_c() +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2")
p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + plot_layout(ncol = 2)
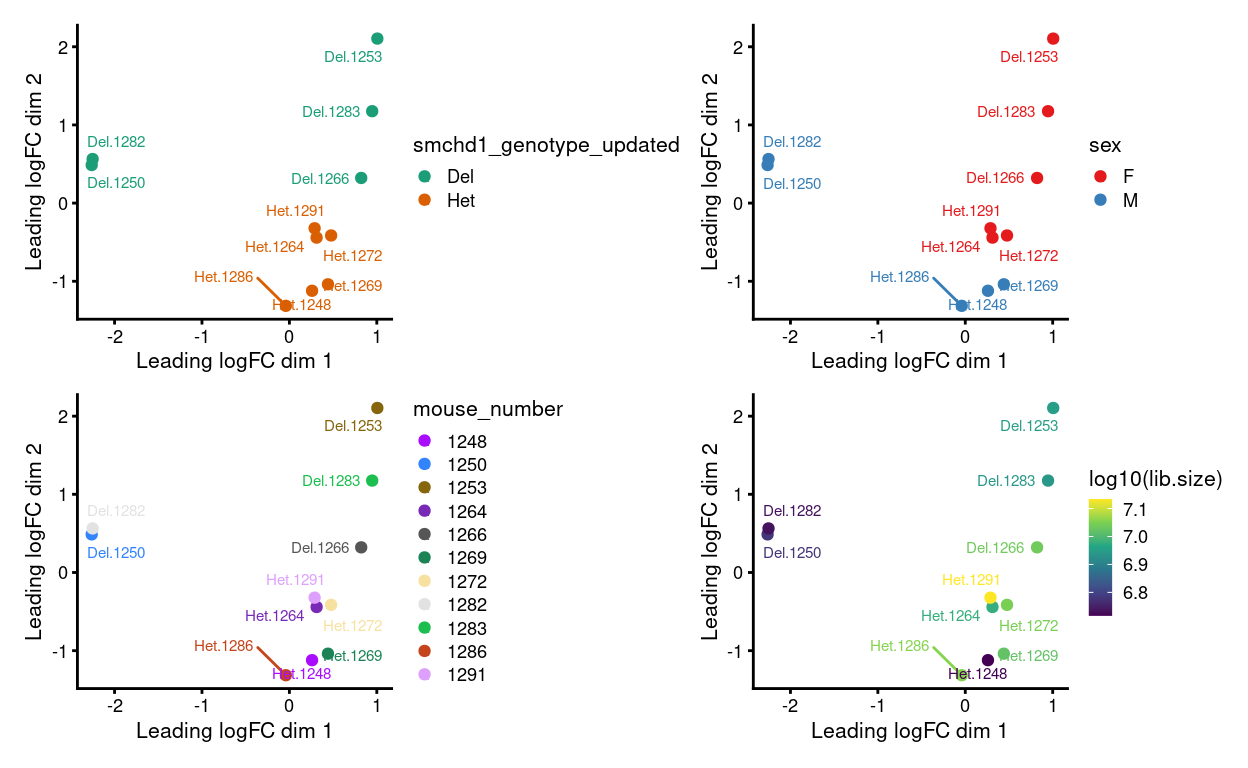
Figure 4: MDS plots of aggregated technical replicates following RUV coloured by various experimental factors.
Gene sets
Marnie and Sarah interested in the following gene sets:
- Non-directional gene sets (i.e. no logFC available from previous data)
X-linked: Anything withENSEMBL.SEQNAMEset as ‘X’).Protocadherin: Genes with symbol of the form Pcdh#.Prader-Willi: Imprinted genes from the Prader-Willi cluster (Ndn, Mkrn3, Peg12)Proliferation Group Venezia (2004): Genes that have their maximum expression at peak-cycling times (Time Of Max = TOM = 2, 3, and 6 days post-treatment) in a time-course experiment designed to stimulate adult HSCs to proliferate (Venezia et al. 2004).- The p-value (ANOVA) is based on about 1500 genes that changed significantly over the time course while the logFC is a separate comparison between FL HSCs (naturally proliferative) and adult HSCs (naturally quiescent).
- We treat this as a non-directional gene set by ignoring the logFC because the specific comparison is not of interest.
Quiescence Group Venezia (2004): Genes that have their maximum expression at non-cycling times (Time Of Max = TOM = 0, 1, 10, and 30 days post-treatment) in a time-course experiment designed to stimulate adult HSCs to proliferate (Venezia et al. 2004).- The p-value (ANOVA) is based on about 1500 genes that changed significantly over the time course while the logFC is a separate comparison between FL HSCs (naturally proliferative) and adult HSCs (naturally quiescent).
- We treat this as a non-directional gene set by ignoring the logFC because the specific comparison is not of interest.
- Directional gene sets (i.e. logFC available from previous data).
Male: Het vs. Del: DEGs from a comparison of male Smchd1-het and Smchd1-del B cells from aged mice (>12 months old)2.Female: Het vs. Del: DEGs from a comparison of female Smchd1-het and Smchd1-del B cells from aged mice (>12 months old)3.Sun (2014): DEGs from a comparison of HSCs from young (2mo) and aged (24mo) male mice (Sun et al. 2014).Chambers (2007): Upregulated DEGs from a comparison of HSCs to an average of all other cell types analysed (Chambers et al. 2007).Gazit (2013): Genes with “enriched expression in HSCs”4 compared with all other hematopoietic cell types (Gazit et al. 2013).- Although no logFC is available, by definition these genes have a logFC > 0.
Chambers (2007) & Gazit (2013): The union ofChambers (2007)andGazit (2013)with the logFC preferentially taken fromChambers (2007).- This is in the spirit of Vizán et al. (2020) who do a gene set enrichment analysis using “a merge of differentially expressed genes provided by
Gazit (2013)andChambers (2007)” but do not explain how they ‘merge’ these gene lists.
- This is in the spirit of Vizán et al. (2020) who do a gene set enrichment analysis using “a merge of differentially expressed genes provided by
Show code
male_het_vs_del <- read.csv(
here("output", "DEGs", "male_B_cells", "male_B_cells.DEGs.csv.gz"))
female_het_vs_del <- read.csv(
here("output", "DEGs", "female_B_cells", "female_B_cells.DEGs.csv.gz"))
# NOTE: The `as.data.frame()` calls are needed because read_excel() returns a
# tibble but `limma::fry()` does not support tibbles.
library(readxl)
sun_2014 <- read_excel(
here("data", "sarahs_gene_lists", "Sun_2014_CellStemCell_DE_HSC_aging.xlsx"),
sheet = "Differentially expressed genes")
sun_2014 <- as.data.frame(sun_2014)
chambers_2007 <- read_excel(
here("data", "sarahs_gene_lists", "HSC_signature_genes.xlsx"),
sheet = "Chambers_2007_CellStemCell",
na = "NA")
chambers_2007 <- as.data.frame(chambers_2007)
gazit_2013 <- read_excel(
here("data", "sarahs_gene_lists", "HSC_signature_genes.xlsx"),
sheet = "Gazit_2013_StemCellRep",
range = "A3:C325")
gazit_2013 <- as.data.frame(gazit_2013)
# NOTE: File manually downloaded from
# https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0020301.st002 and converted to a
# CSV file using LibreOffice.
venezia_proliferation <- read.csv(
here("data", "sarahs_gene_lists", "pbio.0020301.st002.csv"),
header = TRUE,
skip = 1,
nrow = 680)
# NOTE: File manually downloaded from
# https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0020301.st004 and converted to a
# CSV file using LibreOffice.
venezia_quiescence <- read.csv(
here("data", "sarahs_gene_lists", "pbio.0020301.st004.csv"),
header = TRUE,
skip = 1,
nrow = 808)
smchd1_femBcells <- data.table::fread(
here("data", "sarahs_gene_lists", "210923_EdgeR stats p1.0 log2.txt"),
data.table = FALSE)
Analysis of aggregated technical replicates
Show code
y_differences <- makeGroups(
interaction(y$samples$smchd1_genotype_updated, y$samples$sex))
y_ruv <- RUVs(
x = betweenLaneNormalization(y$counts, "upper"),
cIdx = rownames(y),
k = 3,
scIdx = y_differences)
y_design <- model.matrix(
~0 + smchd1_genotype_updated + sex + y_ruv$W,
y$samples)
colnames(y_design) <- sub(
"ruv\\$|smchd1_genotype_updated|sex",
"",
colnames(y_design))
MDS
Show code
y_mds <- plotMDS(cpm(y_ruv$normalizedCounts, log = TRUE), plot = FALSE)
y_df <- cbind(data.frame(x = y_mds$x, y = y_mds$y), y$samples)
rownames(y_df) <- colnames(y)
p1 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = smchd1_genotype_updated, label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = smchd1_genotype_updated_colours)
p2 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = sex, label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = sex_colours)
p3 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = mouse_number, label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = mouse_number_colours)
p4 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = log10(lib.size), label = rownames(y_df)),
data = y_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
scale_colour_viridis_c() +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2")
p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + plot_layout(ncol = 2)
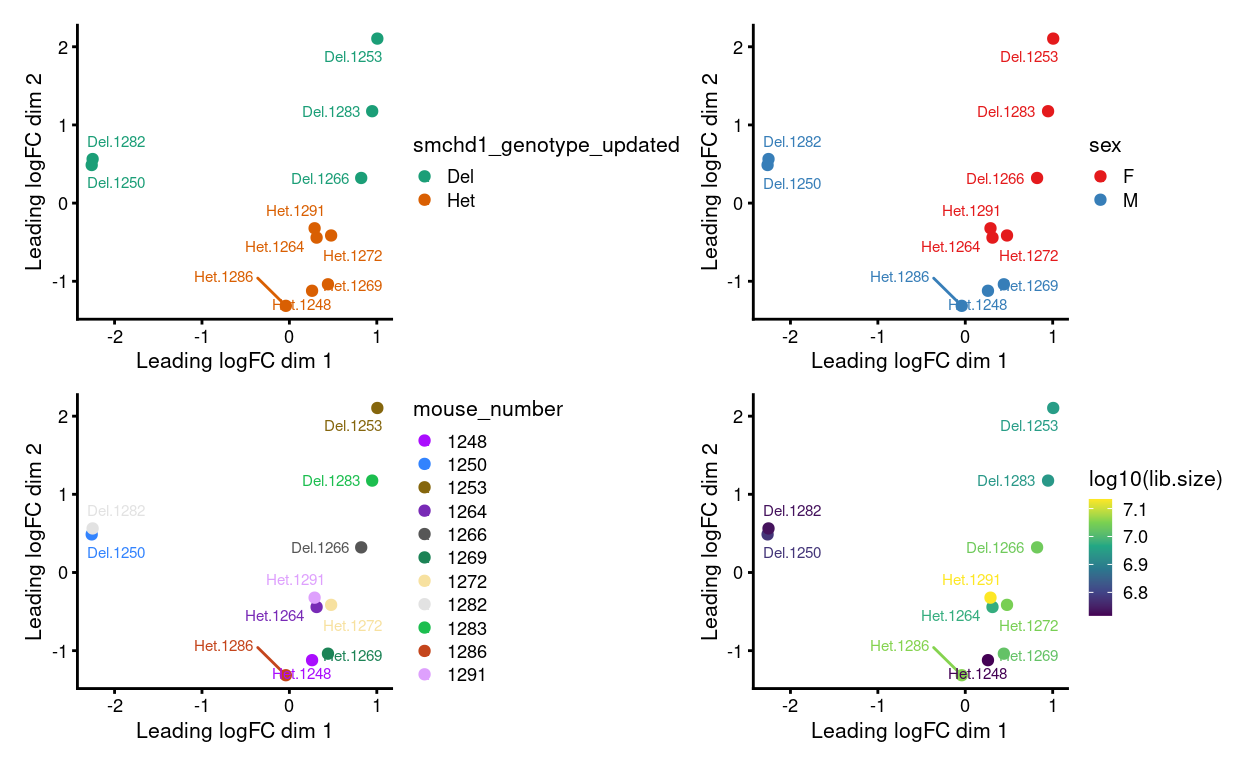
Figure 5: MDS plots of aggregated technical replicates following RUV coloured by various experimental factors.
DE analysis
Fit a model using edgeR with a term for smchd1_genotype_updated and sex.
Show code
y <- estimateDisp(y, y_design)
par(mfrow = c(1, 1))
plotBCV(y)
Show code
| 1Del -1Het | |
|---|---|
| Down | 78 |
| NotSig | 11362 |
| Up | 10 |
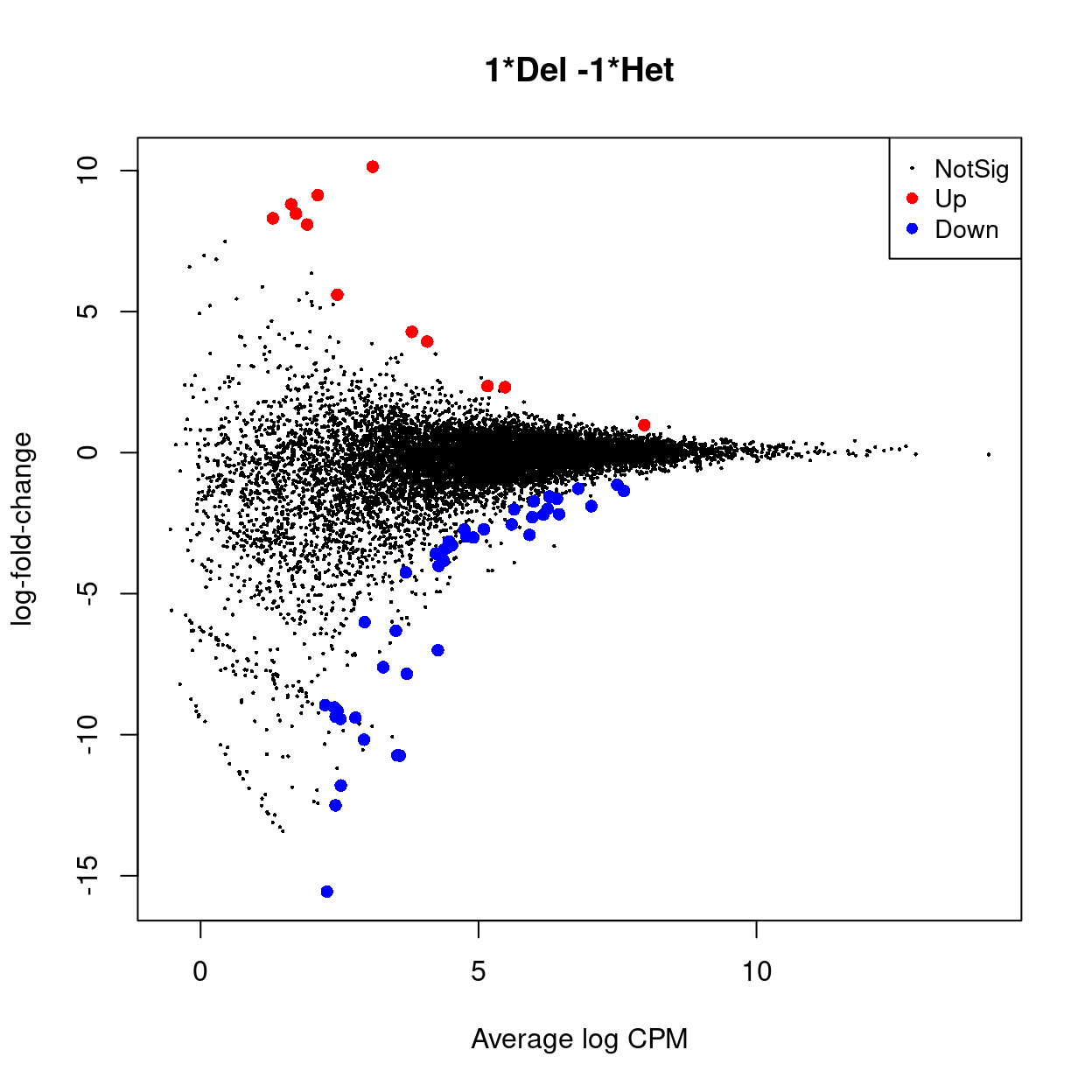
An interactive Glimma MD plot of the differential expression results is available from output/DEGs/reads/glimma-plots/aggregated_tech_reps.md-plot.html.
Show code
CSV file of results available from output/DEGs/reads/.
Figure 7 is a heatmap showing the expression of the DEGs.
Show code
pheatmap(
cpm(y, log = TRUE)[rownames(y_tt), ],
cluster_rows = TRUE,
cluster_cols = FALSE,
color = hcl.colors(101, "Blue-Red 3"),
breaks = seq(-3, 3, length.out = 101),
scale = "row",
annotation_col = data.frame(
genotype = y$samples$smchd1_genotype_updated,
sex = y$samples$sex,
row.names = colnames(y)),
annotation_colors = list(
genotype = smchd1_genotype_updated_colours,
sex = sex_colours),
main = "Male and female samples",
fontsize = 9)
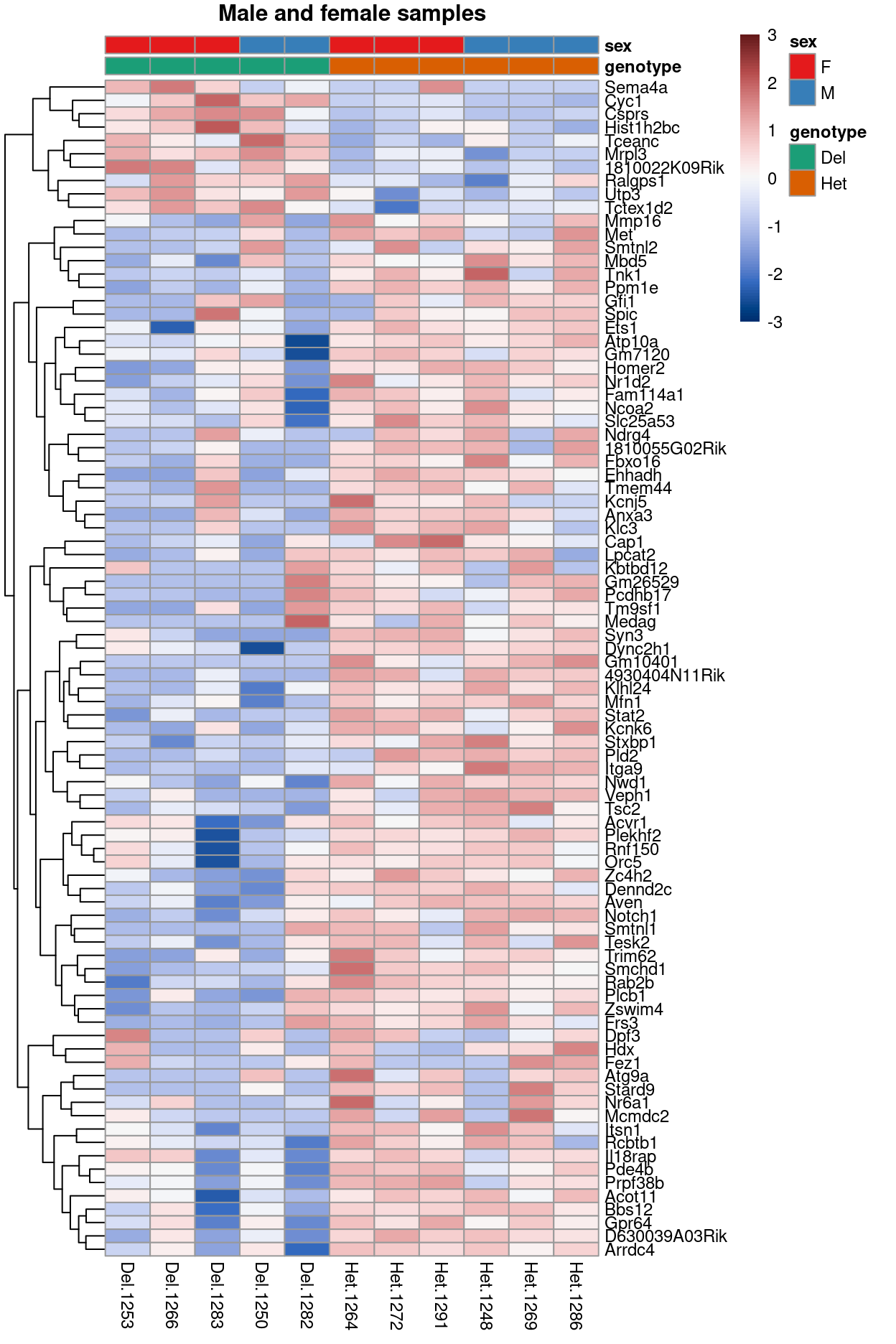
Figure 7: Heatmap of upper-quartile-normalized logCPM values for the DEGs.
Gene set tests
Gene set testing is commonly used to interpret the differential expression results in a biological context. Here we apply various gene set tests to the DEG lists.
goana
We use the goana() function from the limma R/Bioconductor package to test for over-representation of gene ontology (GO) terms in each DEG list.
Show code
list_of_go <- lapply(colnames(y_contrast), function(j) {
dgelrt <- glmLRT(y_dgeglm, contrast = y_contrast[, j])
go <- goana(
de = dgelrt,
geneid = sapply(strsplit(dgelrt$genes$NCBI.ENTREZID, "; "), "[[", 1),
species = "Mm")
gzout <- gzfile(
description = file.path(outdir, "aggregated_tech_reps.goana.csv.gz"),
open = "wb")
write.csv(
topGO(go, number = Inf),
gzout,
row.names = TRUE)
close(gzout)
go
})
names(list_of_go) <- colnames(y_contrast)
CSV files of the results are available from output/DEGs/reads/.
An example of the results are shown below.
Show code
topGO(list_of_go[[1]]) %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = '`goana()` produces a table with a row for each GO term and the following columns: **Term** (GO term); **Ont** (ontology that the GO term belongs to. Possible values are "BP", "CC" and "MF"); **N** (number of genes in the GO term); **Up** (number of up-regulated differentially expressed genes); **Down** (number of down-regulated differentially expressed genes); **P.Up** (p-value for over-representation of GO term in up-regulated genes); **P.Down** (p-value for over-representation of GO term in down-regulated genes)')
| Term | Ont | N | Up | Down | P.Up | P.Down | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0007610 | behavior | BP | 330 | 0 | 10 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000743 |
| GO:0005886 | plasma membrane | CC | 2383 | 2 | 31 | 0.6545710 | 0.0000942 |
| GO:0008277 | regulation of G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway | BP | 73 | 0 | 5 | 1.0000000 | 0.0001331 |
| GO:0071944 | cell periphery | CC | 2469 | 2 | 31 | 0.6758572 | 0.0001873 |
| GO:0006928 | movement of cell or subcellular component | BP | 1156 | 2 | 19 | 0.2716901 | 0.0002006 |
| GO:0060956 | endocardial cell differentiation | BP | 4 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0002710 |
| GO:0060046 | regulation of acrosome reaction | BP | 4 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0002710 |
| GO:0003348 | cardiac endothelial cell differentiation | BP | 5 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0004497 |
| GO:0061343 | cell adhesion involved in heart morphogenesis | BP | 5 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0004497 |
| GO:0045597 | positive regulation of cell differentiation | BP | 670 | 0 | 13 | 1.0000000 | 0.0005275 |
| GO:0072148 | epithelial cell fate commitment | BP | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0006717 |
| GO:0062043 | positive regulation of cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition | BP | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0006717 |
| GO:0062042 | regulation of cardiac epithelial to mesenchymal transition | BP | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0006717 |
| GO:0010717 | regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition | BP | 59 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0006757 |
| GO:0051239 | regulation of multicellular organismal process | BP | 1844 | 1 | 24 | 0.8308213 | 0.0008459 |
| GO:0045153 | electron transporter, transferring electrons within CoQH2-cytochrome c reductase complex activity | MF | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0.0008825 | 1.0000000 |
| GO:0005887 | integral component of plasma membrane | CC | 452 | 1 | 10 | 0.3344946 | 0.0009219 |
| GO:0060973 | cell migration involved in heart development | BP | 7 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0009362 |
| GO:0003198 | epithelial to mesenchymal transition involved in endocardial cushion formation | BP | 7 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0009362 |
| GO:0005523 | tropomyosin binding | MF | 7 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0009362 |
kegga
We use the kegga() function from the limma R/Bioconductor package to test for over-representation of KEGG pathways in each DEG list.
Show code
list_of_kegg <- lapply(colnames(y_contrast), function(j) {
dgelrt <- glmLRT(y_dgeglm, contrast = y_contrast[, j])
kegg <- kegga(
de = dgelrt,
geneid = sapply(strsplit(dgelrt$genes$NCBI.ENTREZID, "; "), "[[", 1),
species = "Mm")
gzout <- gzfile(
description = file.path(outdir, "aggregated_tech_reps.kegga.csv.gz"),
open = "wb")
write.csv(
topKEGG(kegg, number = Inf),
gzout,
row.names = TRUE)
close(gzout)
kegg
})
names(list_of_kegg) <- colnames(y_contrast)
CSV files of the results are available from output/DEGs/reads/.
An example of the results are shown below.
Show code
topKEGG(list_of_kegg[[1]]) %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = '`kegga()` produces a table with a row for each KEGG pathway ID and the following columns: **Pathway** (KEGG pathway); **N** (number of genes in the GO term); **Up** (number of up-regulated differentially expressed genes); **Down** (number of down-regulated differentially expressed genes); **P.Up** (p-value for over-representation of KEGG pathway in up-regulated genes); **P.Down** (p-value for over-representation of KEGG pathway in down-regulated genes)')
| Pathway | N | Up | Down | P.Up | P.Down | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| path:mmu04928 | Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action | 72 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0014987 |
| path:mmu04919 | Thyroid hormone signaling pathway | 95 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0041173 |
| path:mmu04724 | Glutamatergic synapse | 58 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0073758 |
| path:mmu00565 | Ether lipid metabolism | 24 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0117017 |
| path:mmu04915 | Estrogen signaling pathway | 80 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0176377 |
| path:mmu04929 | GnRH secretion | 37 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0266607 |
| path:mmu04072 | Phospholipase D signaling pathway | 101 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0323083 |
| path:mmu05032 | Morphine addiction | 42 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0337172 |
| path:mmu05200 | Pathways in cancer | 352 | 0 | 6 | 1.0000000 | 0.0340336 |
| path:mmu04260 | Cardiac muscle contraction | 47 | 1 | 0 | 0.0407222 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04726 | Serotonergic synapse | 52 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0497017 |
| path:mmu04713 | Circadian entrainment | 53 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0514257 |
| path:mmu04621 | NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | 123 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0527650 |
| path:mmu04925 | Aldosterone synthesis and secretion | 55 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0549374 |
| path:mmu05206 | MicroRNAs in cancer | 129 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0592099 |
| path:mmu05322 | Systemic lupus erythematosus | 75 | 1 | 0 | 0.0642668 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu05165 | Human papillomavirus infection | 221 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0657841 |
| path:mmu04014 | Ras signaling pathway | 136 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0671756 |
| path:mmu05211 | Renal cell carcinoma | 62 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0678581 |
| path:mmu00564 | Glycerophospholipid metabolism | 65 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0736747 |
camera with MSigDB gene sets
We use the camera() function from the limma R/Bioconductor package to test whether a set of genes is highly ranked relative to other genes in terms of differential expression, accounting for inter-gene correlation. Specifically, we test using gene sets from MSigDB, namely:
- H: hallmark gene sets are coherently expressed signatures derived by aggregating many MSigDB gene sets to represent well-defined biological states or processes.
- C2: curated gene sets from online pathway databases, publications in PubMed, and knowledge of domain experts.
Show code
# NOTE: Using BiocFileCache to avoid re-downloading these gene sets everytime
# the report is rendered.
library(BiocFileCache)
bfc <- BiocFileCache()
# NOTE: Creating list of gene sets in this slightly convoluted way so that each
# gene set name is prepended by its origin (e.g. H, C2, or C7).
msigdb <- do.call(
c,
list(
H = readRDS(
bfcrpath(
bfc,
"http://bioinf.wehi.edu.au/MSigDB/v7.1/Mm.h.all.v7.1.entrez.rds")),
C2 = readRDS(
bfcrpath(
bfc,
"http://bioinf.wehi.edu.au/MSigDB/v7.1/Mm.c2.all.v7.1.entrez.rds"))))
y_idx <- ids2indices(
msigdb,
id = sapply(strsplit(y$genes$NCBI.ENTREZID, "; "), "[[", 1))
list_of_camera <- lapply(colnames(y_contrast), function(j) {
cam <- camera(
y = y,
index = y_idx,
design = y_design,
contrast = y_contrast[, j])
gzout <- gzfile(
description = file.path(outdir, "aggregated_tech_reps.camera.csv.gz"),
open = "wb")
write.csv(
cam,
gzout,
row.names = TRUE)
close(gzout)
cam
})
names(list_of_camera) <- colnames(y_contrast)
CSV files of the results are available from output/DEGs/reads.
An example of the results are shown below.
Show code
head(list_of_camera[[1]]) %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = '`camera()` produces a table with a row for each gene set (prepended by which MSigDB collection it comes from) and the following columns: **NGenes** (number of genes in set); **Direction** (direction of change); **PValue** (two-tailed p-value); **FDR** (Benjamini and Hochberg FDR adjusted p-value).')
| NGenes | Direction | PValue | FDR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2.KEGG_RIBOSOME | 102 | Up | 0 | 6.0e-07 |
| C2.REACTOME_EUKARYOTIC_TRANSLATION_ELONGATION | 107 | Up | 0 | 2.3e-06 |
| C2.REACTOME_SRP_DEPENDENT_COTRANSLATIONAL_PROTEIN_TARGETING_TO_MEMBRANE | 130 | Up | 0 | 4.4e-06 |
| C2.REACTOME_RESPIRATORY_ELECTRON_TRANSPORT_ATP_SYNTHESIS_BY_CHEMIOSMOTIC_COUPLING_AND_HEAT_PRODUCTION_BY_UNCOUPLING_PROTEINS | 120 | Up | 0 | 4.4e-06 |
| C2.REACTOME_RESPONSE_OF_EIF2AK4_GCN2_TO_AMINO_ACID_DEFICIENCY | 115 | Up | 0 | 4.4e-06 |
| C2.REACTOME_EUKARYOTIC_TRANSLATION_INITIATION | 139 | Up | 0 | 4.4e-06 |
Sarah’s gene lists
Show code
y_X <- y$genes$ENSEMBL.SEQNAME == "X"
y_protocadherin <- grepl("Pcdh", rownames(y))
y_pw <- rownames(y) %in% c("Ndn", "Mkrn3", "Peg12")
y_male <- male_het_vs_del[
male_het_vs_del$FDR < 0.05,
c("ENSEMBL.SYMBOL", "logFC")]
y_female <- male_het_vs_del[
female_het_vs_del$FDR < 0.05,
c("ENSEMBL.SYMBOL", "logFC")]
y_sun <- sun_2014[, c("geneSymbol", "log2FC")]
y_chambers <- chambers_2007[, c("Gene Symbol", "Fold Difference")]
y_chambers$logFC <- log2(y_chambers$`Fold Difference`)
y_chambers$`Fold Difference` <- NULL
y_chambers <- y_chambers[!is.na(y_chambers$`Gene Symbol`), ]
y_chambers <- y_chambers[!duplicated(y_chambers$`Gene Symbol`), ]
y_gazit <- gazit_2013[, c("Symbol"), drop = FALSE]
y_gazit$Symbol <- paste(
substring(y_gazit$Symbol, 1, 1),
tolower(substring(y_gazit$Symbol, 2)),
sep = "")
y_gazit$logFC <- 1
y_chambers_gazit <- data.frame(
Symbol = c(y_chambers$`Gene Symbol`, y_gazit$Symbol),
logFC = c(y_chambers$logFC, y_gazit$logFC))
y_chambers_gazit <- y_chambers_gazit[!duplicated(y_chambers_gazit$Symbol), ]
y_venezia_proliferation <- rownames(y) %in% venezia_proliferation$Gene.Symbol
y_venezia_quiescence <- rownames(y) %in% venezia_quiescence$Gene.Symbol
y_index <- list(
`X-linked` = y_X,
Protocadherin = y_protocadherin,
`Prader-Willi` = y_pw,
`Male: Het vs. Del` = y_male,
`Female: Het vs. Del` = y_female,
`Sun (2014)` = y_sun,
`Chambers (2007)` = y_chambers,
`Gazit (2013)` = y_gazit,
`Chambers (2007) & Gazit (2013)` = y_chambers_gazit,
`Proliferation Group Venezia (2004)` = y_venezia_proliferation,
`Quiescence Group Venezia (2004)` = y_venezia_quiescence)
Sarah requested testing a number of gene sets (see Gene sets).
We use the fry() function from the edgeR R/Bioconductor package to perform a self-contained gene set test against the null hypothesis that none of the genes in the set are differentially expressed.
Show code
fry(
y,
index = y_index,
design = y_design,
contrast = y_contrast,
sort = "none") %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = "Results of applying `fry()` to the RNA-seq differential expression results using the supplied gene sets. A significant 'Up' P-value means that the differential expression results found in the RNA-seq data are positively correlated with the expression signature from the corresponding gene set. Conversely, a significant 'Down' P-value means that the differential expression log-fold-changes are negatively correlated with the expression signature from the corresponding gene set. A significant 'Mixed' P-value means that the genes in the set tend to be differentially expressed without regard for direction.")
| NGenes | Direction | PValue | FDR | PValue.Mixed | FDR.Mixed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-linked | 388 | Down | 0.4732142 | 0.4732142 | 0.0000240 | 0.0002641 |
| Protocadherin | 4 | Down | 0.1818142 | 0.2499945 | 0.0359534 | 0.0395488 |
| Prader-Willi | 3 | Up | 0.2856524 | 0.3491307 | 0.4549877 | 0.4549877 |
| Male: Het vs. Del | 7 | Up | 0.0159925 | 0.0433171 | 0.0000583 | 0.0003203 |
| Female: Het vs. Del | 17 | Up | 0.1731703 | 0.2499945 | 0.0001075 | 0.0003203 |
| Sun (2014) | 1997 | Down | 0.3728438 | 0.4101281 | 0.0004929 | 0.0007745 |
| Chambers (2007) | 208 | Down | 0.0036999 | 0.0289609 | 0.0001395 | 0.0003203 |
| Gazit (2013) | 249 | Down | 0.0430404 | 0.0789075 | 0.0094767 | 0.0115826 |
| Chambers (2007) & Gazit (2013) | 404 | Down | 0.0066715 | 0.0289609 | 0.0001456 | 0.0003203 |
| Proliferation Group Venezia (2004) | 365 | Up | 0.0078984 | 0.0289609 | 0.0009692 | 0.0013326 |
| Quiescence Group Venezia (2004) | 382 | Down | 0.0196896 | 0.0433171 | 0.0003511 | 0.0006437 |
Show code
par(mfrow = c(length(y_index), 2))
for (n in names(y_index)) {
if (is.data.frame(y_index[[n]])) {
y_status <- rep(0, nrow(y_dgelrt))
y_status[rownames(y) %in% y_index[[n]][, 1]] <-
sign(y_index[[n]][y_index[[n]][, 1] %in% rownames(y), 2])
plotMD(
y_dgelrt,
status = y_status,
hl.col = c("red", "blue"),
legend = "bottomright",
main = n)
abline(h = 0, col = "darkgrey")
} else {
y_status <- rep("Other", nrow(y_dgelrt))
y_status[y_index[[n]]] <- n
plotMD(
y_dgelrt,
status = y_status,
values = n,
hl.col = "red",
legend = "bottomright",
main = n)
abline(h = 0, col = "darkgrey")
}
if (is.data.frame(y_index[[n]])) {
barcodeplot(
y_dgelrt$table$logFC,
rownames(y) %in% y_index[[n]][, 1],
gene.weights = y_index[[n]][
y_index[[n]][, 1] %in% rownames(y), 2])
} else {
barcodeplot(
y_dgelrt$table$logFC,
y_index[[n]])
}
}
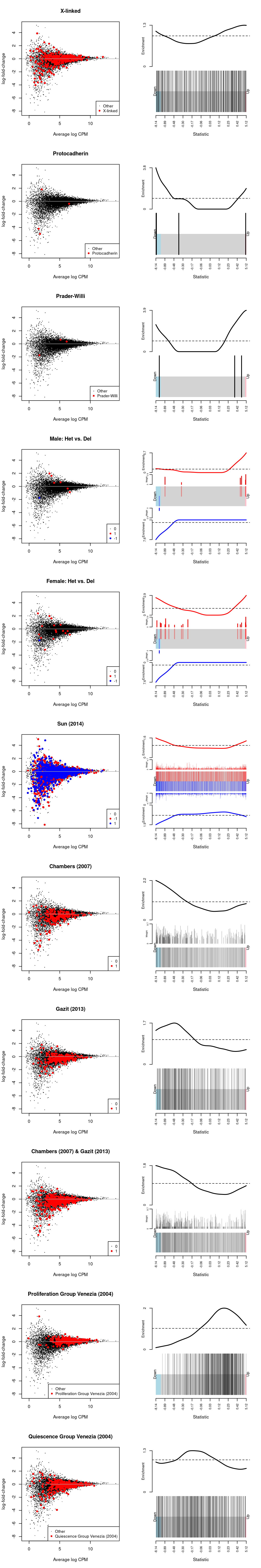
Figure 8: MD-plot and barcode plot of DEGs in supplied gene sets. Directional gene sets have (1) MD plot points coloured according to the statistical significance of the gene in the gene set (2) barcode plot ‘weights’ given by the logFC of the gene in the gene set. For the barcode plot, genes are represented by bars and are ranked from left to right by increasing log-fold change. This forms the barcode-like pattern. The line (or worm) above the barcode shows the relative local enrichment of the vertical bars in each part of the plot. The dotted horizontal line indicates neutral enrichment; the worm above the dotted line shows enrichment while the worm below the dotted line shows depletion.
Male-only: analysis of aggregated technical replicates
Show code
ym_differences <- makeGroups(ym$samples$smchd1_genotype_updated)
ym_ruv <- RUVs(
x = betweenLaneNormalization(ym$counts, "upper"),
cIdx = rownames(ym),
k = 1,
scIdx = ym_differences)
ym_design <- model.matrix(
~0 + smchd1_genotype_updated + ym_ruv$W,
ym$samples)
colnames(ym_design) <- sub(
"ruv\\$|smchd1_genotype_updated",
"",
colnames(ym_design))
MDS
Show code
ym_mds <- plotMDS(cpm(ym_ruv$normalizedCounts, log = TRUE), plot = FALSE)
ym_df <- cbind(data.frame(x = ym_mds$x, y = ym_mds$y), ym$samples)
rownames(ym_df) <- colnames(ym)
p1 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = smchd1_genotype_updated, label = rownames(ym_df)),
data = ym_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = smchd1_genotype_updated_colours)
p2 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = sex, label = rownames(ym_df)),
data = ym_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = sex_colours)
p3 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = mouse_number, label = rownames(ym_df)),
data = ym_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = mouse_number_colours)
p4 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = log10(lib.size), label = rownames(ym_df)),
data = ym_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
scale_colour_viridis_c() +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2")
p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + plot_layout(ncol = 2)
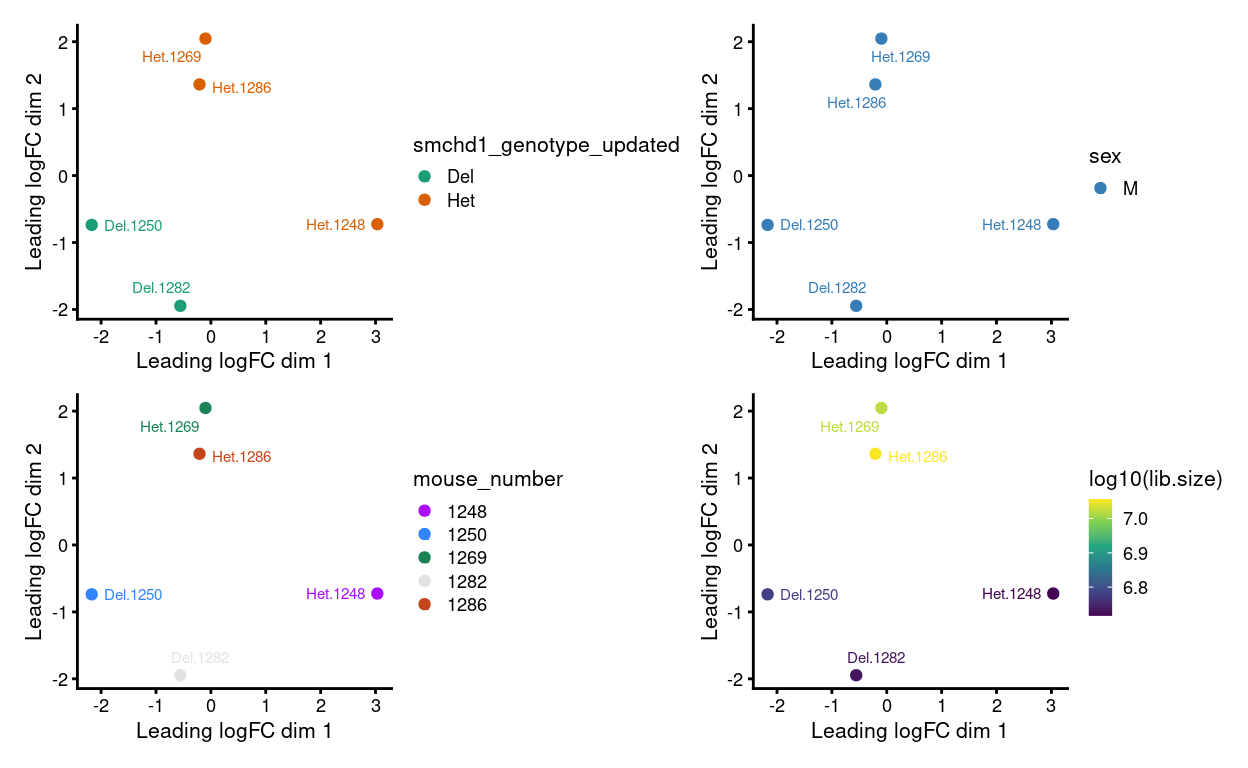
Figure 9: MDS plots of aggregated technical replicates following RUV coloured by various experimental factors.
DE analysis
Fit a model using edgeR with a term for smchd1_genotype_updated.
Show code
ym <- estimateDisp(ym, ym_design)
par(mfrow = c(1, 1))
plotBCV(ym)
Show code
| 1Del -1Het | |
|---|---|
| Down | 44 |
| NotSig | 11543 |
| Up | 12 |
An interactive Glimma MD plot of the differential expression results is available from output/DEGs/reads/glimma-plots/aggregated_tech_reps.males.md-plot.html.
Show code
ym_tt <- topTags(ym_dgelrt, n = Inf, sort.by = "none")
glMDPlot(
x = ym_dgelrt,
counts = ym,
anno = ym$genes,
display.columns = c("ENSEMBL.SYMBOL"),
groups = ym$samples$group,
samples = colnames(ym),
status = ym_dt,
transform = TRUE,
sample.cols = ym$samples$smchd1_genotype_updated_colours,
path = outdir,
html = "aggregated_tech_reps.males.md-plot",
launch = FALSE)
CSV file of results available from output/DEGs/reads/aggregated_tech_reps.males.DEGs.csv.gz.
Figure 11 is a heatmap showing the expression of the DEGs.
Show code
pheatmap(
cpm(ym, log = TRUE)[rownames(ym_tt), ],
cluster_rows = TRUE,
cluster_cols = FALSE,
color = hcl.colors(101, "Blue-Red 3"),
breaks = seq(-3, 3, length.out = 101),
scale = "row",
annotation_col = data.frame(
genotype = ym$samples$smchd1_genotype_updated,
sex = ym$samples$sex,
row.names = colnames(ym)),
annotation_colors = list(
genotype = smchd1_genotype_updated_colours,
sex = sex_colours),
main = "Male samples",
fontsize = 9)
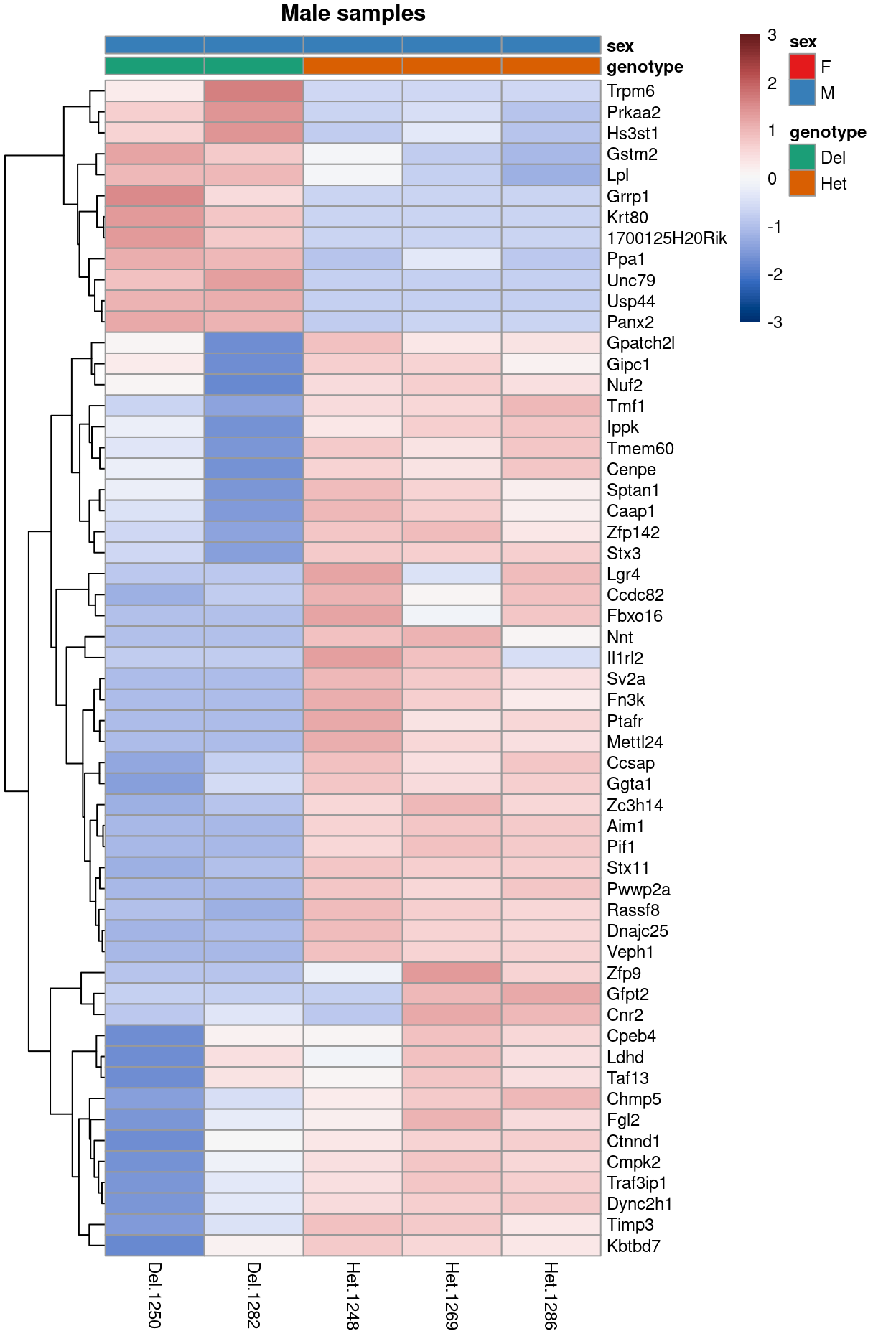
Figure 11: Heatmap of upper-quartile-normalzied logCPM values for the DEGs.
Gene set tests
Gene set testing is commonly used to interpret the differential expression results in a biological context. Here we apply various gene set tests to the DEG lists.
goana
We use the goana() function from the limma R/Bioconductor package to test for over-representation of gene ontology (GO) terms in each DEG list.
Show code
list_of_go <- lapply(colnames(ym_contrast), function(j) {
dgelrt <- glmLRT(ym_dgeglm, contrast = ym_contrast[, j])
go <- goana(
de = dgelrt,
geneid = sapply(strsplit(dgelrt$genes$NCBI.ENTREZID, "; "), "[[", 1),
species = "Mm")
gzout <- gzfile(
description = file.path(outdir, "aggregated_tech_reps.males.goana.csv.gz"),
open = "wb")
write.csv(
topGO(go, number = Inf),
gzout,
row.names = TRUE)
close(gzout)
go
})
names(list_of_go) <- colnames(ym_contrast)
CSV files of the results are available from output/DEGs/reads/.
An example of the results are shown below.
Show code
topGO(list_of_go[[1]]) %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = '`goana()` produces a table with a row for each GO term and the following columns: **Term** (GO term); **Ont** (ontology that the GO term belongs to. Possible values are "BP", "CC" and "MF"); **N** (number of genes in the GO term); **Up** (number of up-regulated differentially expressed genes); **Down** (number of down-regulated differentially expressed genes); **P.Up** (p-value for over-representation of GO term in up-regulated genes); **P.Down** (p-value for over-representation of GO term in down-regulated genes)')
| Term | Ont | N | Up | Down | P.Up | P.Down | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0048786 | presynaptic active zone | CC | 48 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000323 |
| GO:0006633 | fatty acid biosynthetic process | BP | 92 | 3 | 0 | 0.0001039 | 1.0000000 |
| GO:0016079 | synaptic vesicle exocytosis | BP | 70 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0001431 |
| GO:0099568 | cytoplasmic region | CC | 134 | 0 | 5 | 1.0000000 | 0.0001514 |
| GO:0072330 | monocarboxylic acid biosynthetic process | BP | 113 | 3 | 0 | 0.0001914 | 1.0000000 |
| GO:0071398 | cellular response to fatty acid | BP | 21 | 2 | 0 | 0.0002080 | 1.0000000 |
| GO:0045055 | regulated exocytosis | BP | 147 | 0 | 5 | 1.0000000 | 0.0002334 |
| GO:0043207 | response to external biotic stimulus | BP | 715 | 1 | 10 | 0.5378743 | 0.0002948 |
| GO:0051707 | response to other organism | BP | 715 | 1 | 10 | 0.5378743 | 0.0002948 |
| GO:0009607 | response to biotic stimulus | BP | 739 | 1 | 10 | 0.5500911 | 0.0003843 |
| GO:0007269 | neurotransmitter secretion | BP | 94 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0004451 |
| GO:0099643 | signal release from synapse | BP | 94 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0004451 |
| GO:0070542 | response to fatty acid | BP | 31 | 2 | 0 | 0.0004578 | 1.0000000 |
| GO:0007080 | mitotic metaphase plate congression | BP | 40 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0004699 |
| GO:0032838 | plasma membrane bounded cell projection cytoplasm | CC | 102 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0006066 |
| GO:0007052 | mitotic spindle organization | BP | 103 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0006294 |
| GO:0043312 | neutrophil degranulation | BP | 10 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0006334 |
| GO:0030425 | dendrite | CC | 395 | 1 | 7 | 0.3431457 | 0.0006892 |
| GO:0097447 | dendritic tree | CC | 396 | 1 | 7 | 0.3438566 | 0.0006996 |
| GO:0046394 | carboxylic acid biosynthetic process | BP | 184 | 3 | 0 | 0.0008007 | 1.0000000 |
kegga
We use the kegga() function from the limma R/Bioconductor package to test for over-representation of KEGG pathways in each DEG list.
Show code
list_of_kegg <- lapply(colnames(ym_contrast), function(j) {
dgelrt <- glmLRT(ym_dgeglm, contrast = ym_contrast[, j])
kegg <- kegga(
de = dgelrt,
geneid = sapply(strsplit(dgelrt$genes$NCBI.ENTREZID, "; "), "[[", 1),
species = "Mm")
gzout <- gzfile(
description = file.path(outdir, "aggregated_tech_reps.males.kegga.csv.gz"),
open = "wb")
write.csv(
topKEGG(kegg, number = Inf),
gzout,
row.names = TRUE)
close(gzout)
kegg
})
names(list_of_kegg) <- colnames(ym_contrast)
CSV files of the results are available from output/DEGs/reads/.
An example of the results are shown below.
Show code
topKEGG(list_of_kegg[[1]]) %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = '`kegga()` produces a table with a row for each KEGG pathway ID and the following columns: **Pathway** (KEGG pathway); **N** (number of genes in the GO term); **Up** (number of up-regulated differentially expressed genes); **Down** (number of down-regulated differentially expressed genes); **P.Up** (p-value for over-representation of KEGG pathway in up-regulated genes); **P.Down** (p-value for over-representation of KEGG pathway in down-regulated genes)')
| Pathway | N | Up | Down | P.Up | P.Down | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| path:mmu05418 | Fluid shear stress and atherosclerosis | 106 | 2 | 0 | 0.0052450 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04130 | SNARE interactions in vesicular transport | 31 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0062180 |
| path:mmu00534 | Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis - heparan sulfate / heparin | 15 | 1 | 0 | 0.0155706 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04080 | Neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction | 53 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0174721 |
| path:mmu00982 | Drug metabolism - cytochrome P450 | 22 | 1 | 0 | 0.0227606 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu05204 | Chemical carcinogenesis - DNA adducts | 23 | 1 | 0 | 0.0237838 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu00980 | Metabolism of xenobiotics by cytochrome P450 | 25 | 1 | 0 | 0.0258272 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04979 | Cholesterol metabolism | 28 | 1 | 0 | 0.0288851 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04710 | Circadian rhythm | 28 | 1 | 0 | 0.0288851 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04978 | Mineral absorption | 28 | 1 | 0 | 0.0288851 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu00561 | Glycerolipid metabolism | 40 | 1 | 0 | 0.0410286 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu03320 | PPAR signaling pathway | 41 | 1 | 0 | 0.0420342 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu05410 | Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy | 44 | 1 | 0 | 0.0450454 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu00601 | Glycosphingolipid biosynthesis - lacto and neolacto series | 12 | 0 | 1 | 1.0000000 | 0.0450454 |
| path:mmu00983 | Drug metabolism - other enzymes | 46 | 1 | 0 | 0.0470480 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04213 | Longevity regulating pathway - multiple species | 48 | 1 | 0 | 0.0490468 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04920 | Adipocytokine signaling pathway | 49 | 1 | 0 | 0.0500447 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu00480 | Glutathione metabolism | 50 | 1 | 0 | 0.0510417 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu01524 | Platinum drug resistance | 65 | 1 | 0 | 0.0658817 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04211 | Longevity regulating pathway | 71 | 1 | 0 | 0.0717580 | 1.0000000 |
camera with MSigDB gene sets
We use the camera() function from the limma R/Bioconductor package to test whether a set of genes is highly ranked relative to other genes in terms of differential expression, accounting for inter-gene correlation. Specifically, we test using gene sets from MSigDB, namely:
- H: hallmark gene sets are coherently expressed signatures derived by aggregating many MSigDB gene sets to represent well-defined biological states or processes.
- C2: curated gene sets from online pathway databases, publications in PubMed, and knowledge of domain experts.
Show code
ym_idx <- ids2indices(
msigdb,
id = sapply(strsplit(ym$genes$NCBI.ENTREZID, "; "), "[[", 1))
list_of_camera <- lapply(colnames(ym_contrast), function(j) {
cam <- camera(
y = ym,
index = ym_idx,
design = ym_design,
contrast = ym_contrast[, j])
gzout <- gzfile(
description = file.path(outdir, "aggregated_tech_reps.males.camera.csv.gz"),
open = "wb")
write.csv(
cam,
gzout,
row.names = TRUE)
close(gzout)
cam
})
names(list_of_camera) <- colnames(ym_contrast)
CSV files of the results are available from output/DEGs/reads.
An example of the results are shown below.
Show code
head(list_of_camera[[1]]) %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = '`camera()` produces a table with a row for each gene set (prepended by which MSigDB collection it comes from) and the following columns: **NGenes** (number of genes in set); **Direction** (direction of change); **PValue** (two-tailed p-value); **FDR** (Benjamini and Hochberg FDR adjusted p-value).')
| NGenes | Direction | PValue | FDR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H.HALLMARK_MYC_TARGETS_V1 | 229 | Up | 0.0000535 | 0.2203915 |
| C2.JOHANSSON_GLIOMAGENESIS_BY_PDGFB_DN | 19 | Down | 0.0000794 | 0.2203915 |
| C2.REACTOME_ELECTRIC_TRANSMISSION_ACROSS_GAP_JUNCTIONS | 2 | Up | 0.0001400 | 0.2592181 |
| C2.RAHMAN_TP53_TARGETS_PHOSPHORYLATED | 25 | Up | 0.0002956 | 0.3456734 |
| C2.REACTOME_UNWINDING_OF_DNA | 12 | Up | 0.0003112 | 0.3456734 |
| C2.PID_MYC_ACTIV_PATHWAY | 95 | Up | 0.0003762 | 0.3482163 |
Sarah’s gene lists
Show code
ym_X <- ym$genes$ENSEMBL.SEQNAME == "X"
ym_protocadherin <- grepl("Pcdh", rownames(ym))
ym_pw <- rownames(ym) %in% c("Ndn", "Mkrn3", "Peg12")
ym_male <- male_het_vs_del[
male_het_vs_del$FDR < 0.05,
c("ENSEMBL.SYMBOL", "logFC")]
ym_female <- male_het_vs_del[
female_het_vs_del$FDR < 0.05,
c("ENSEMBL.SYMBOL", "logFC")]
ym_sun <- sun_2014[, c("geneSymbol", "log2FC")]
ym_chambers <- chambers_2007[, c("Gene Symbol", "Fold Difference")]
ym_chambers$logFC <- log2(ym_chambers$`Fold Difference`)
ym_chambers$`Fold Difference` <- NULL
ym_chambers <- ym_chambers[!is.na(ym_chambers$`Gene Symbol`), ]
ym_chambers <- ym_chambers[!duplicated(ym_chambers$`Gene Symbol`), ]
ym_gazit <- gazit_2013[, c("Symbol"), drop = FALSE]
ym_gazit$Symbol <- paste(
substring(ym_gazit$Symbol, 1, 1),
tolower(substring(ym_gazit$Symbol, 2)),
sep = "")
ym_gazit$logFC <- 1
ym_chambers_gazit <- data.frame(
Symbol = c(ym_chambers$`Gene Symbol`, ym_gazit$Symbol),
logFC = c(ym_chambers$logFC, ym_gazit$logFC))
ym_chambers_gazit <- ym_chambers_gazit[!duplicated(ym_chambers_gazit$Symbol), ]
ym_venezia_proliferation <- rownames(ym) %in% venezia_proliferation$Gene.Symbol
ym_venezia_quiescence <- rownames(ym) %in% venezia_quiescence$Gene.Symbol
ym_index <- list(
`X-linked` = ym_X,
Protocadherin = ym_protocadherin,
`Prader-Willi` = ym_pw,
`Male: Het vs. Del` = ym_male,
`Female: Het vs. Del` = ym_female,
`Sun (2014)` = ym_sun,
`Chambers (2007)` = ym_chambers,
`Gazit (2013)` = ym_gazit,
`Chambers (2007) & Gazit (2013)` = ym_chambers_gazit,
`Proliferation Group Venezia (2004)` = ym_venezia_proliferation,
`Quiescence Group Venezia (2004)` = ym_venezia_quiescence)
Sarah requested testing a number of gene sets (see Gene sets).
We use the fry() function from the edgeR R/Bioconductor package to perform a self-contained gene set test against the null hypothesis that none of the genes in the set are differentially expressed.
Show code
fry(
ym,
index = ym_index,
design = ym_design,
contrast = ym_contrast,
sort = "none") %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = "Results of applying `fry()` to the RNA-seq differential expression results using the supplied gene sets. A significant 'Up' P-value means that the differential expression results found in the RNA-seq data are positively correlated with the expression signature from the corresponding gene set. Conversely, a significant 'Down' P-value means that the differential expression log-fold-changes are negatively correlated with the expression signature from the corresponding gene set. A significant 'Mixed' P-value means that the genes in the set tend to be differentially expressed without regard for direction.")
| NGenes | Direction | PValue | FDR | PValue.Mixed | FDR.Mixed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-linked | 392 | Down | 0.0346948 | 0.1056738 | 0.0085836 | 0.0157366 |
| Protocadherin | 6 | Up | 0.3718805 | 0.5843836 | 0.0278469 | 0.0437594 |
| Prader-Willi | 3 | Up | 0.5392710 | 0.6210234 | 0.0766661 | 0.0843327 |
| Male: Het vs. Del | 8 | Up | 0.5645667 | 0.6210234 | 0.2702930 | 0.2702930 |
| Female: Het vs. Del | 19 | Up | 0.4705836 | 0.6210234 | 0.0074240 | 0.0157366 |
| Sun (2014) | 2023 | Up | 0.7412489 | 0.7412489 | 0.0029447 | 0.0081364 |
| Chambers (2007) | 206 | Down | 0.0047591 | 0.0261751 | 0.0029587 | 0.0081364 |
| Gazit (2013) | 248 | Down | 0.1999566 | 0.3665871 | 0.0007036 | 0.0077392 |
| Chambers (2007) & Gazit (2013) | 402 | Down | 0.0030405 | 0.0261751 | 0.0028950 | 0.0081364 |
| Proliferation Group Venezia (2004) | 364 | Up | 0.0480335 | 0.1056738 | 0.0698494 | 0.0843327 |
| Quiescence Group Venezia (2004) | 383 | Down | 0.0410618 | 0.1056738 | 0.0366139 | 0.0503441 |
Show code
par(mfrow = c(length(ym_index), 2))
for (n in names(ym_index)) {
if (is.data.frame(ym_index[[n]])) {
ym_status <- rep(0, nrow(ym_dgelrt))
ym_status[rownames(ym) %in% ym_index[[n]][, 1]] <-
sign(ym_index[[n]][ym_index[[n]][, 1] %in% rownames(ym), 2])
plotMD(
ym_dgelrt,
status = ym_status,
hl.col = c("red", "blue"),
legend = "bottomright",
main = n)
abline(h = 0, col = "darkgrey")
} else {
ym_status <- rep("Other", nrow(ym_dgelrt))
ym_status[ym_index[[n]]] <- n
plotMD(
ym_dgelrt,
status = ym_status,
values = n,
hl.col = "red",
legend = "bottomright",
main = n)
abline(h = 0, col = "darkgrey")
}
if (is.data.frame(ym_index[[n]])) {
barcodeplot(
ym_dgelrt$table$logFC,
rownames(ym) %in% ym_index[[n]][, 1],
gene.weights = ym_index[[n]][
ym_index[[n]][, 1] %in% rownames(ym), 2])
} else {
barcodeplot(
ym_dgelrt$table$logFC,
ym_index[[n]])
}
}
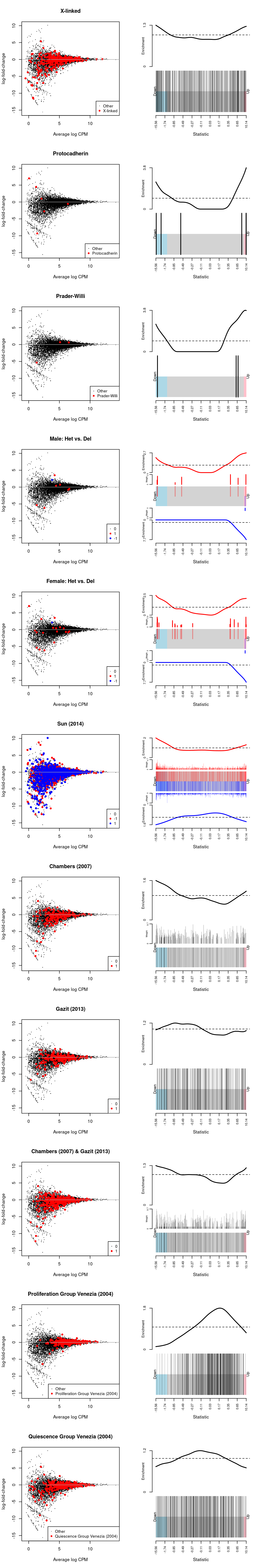
Figure 12: MD-plot and barcode plot of DEGs in supplied gene sets. Directional gene sets have (1) MD plot points coloured according to the statistical significance of the gene in the gene set (2) barcode plot ‘weights’ given by the logFC of the gene in the gene set. For the barcode plot, genes are represented by bars and are ranked from left to right by increasing log-fold change. This forms the barcode-like pattern. The line (or worm) above the barcode shows the relative local enrichment of the vertical bars in each part of the plot. The dotted horizontal line indicates neutral enrichment; the worm above the dotted line shows enrichment while the worm below the dotted line shows depletion.
Female-only: analysis of aggregated technical replicates
Show code
yf_differences <- makeGroups(yf$samples$smchd1_genotype_updated)
yf_ruv <- RUVs(
x = betweenLaneNormalization(yf$counts, "upper"),
cIdx = rownames(yf),
k = 1,
scIdx = yf_differences)
yf_design <- model.matrix(
~0 + smchd1_genotype_updated + yf_ruv$W,
yf$samples)
colnames(yf_design) <- sub(
"ruv\\$|smchd1_genotype_updated",
"",
colnames(yf_design))
MDS
Show code
yf_mds <- plotMDS(cpm(yf_ruv$normalizedCounts, log = TRUE), plot = FALSE)
yf_df <- cbind(data.frame(x = yf_mds$x, y = yf_mds$y), yf$samples)
rownames(yf_df) <- colnames(yf)
p1 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = smchd1_genotype_updated, label = rownames(yf_df)),
data = yf_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = smchd1_genotype_updated_colours)
p2 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = sex, label = rownames(yf_df)),
data = yf_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = sex_colours)
p3 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = mouse_number, label = rownames(yf_df)),
data = yf_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2") +
scale_colour_manual(values = mouse_number_colours)
p4 <- ggplot(
aes(x = x, y = y, colour = log10(lib.size), label = rownames(yf_df)),
data = yf_df) +
geom_point() +
geom_text_repel(size = 2) +
theme_cowplot(font_size = 8) +
scale_colour_viridis_c() +
xlab("Leading logFC dim 1") +
ylab("Leading logFC dim 2")
p1 + p2 + p3 + p4 + plot_layout(ncol = 2)
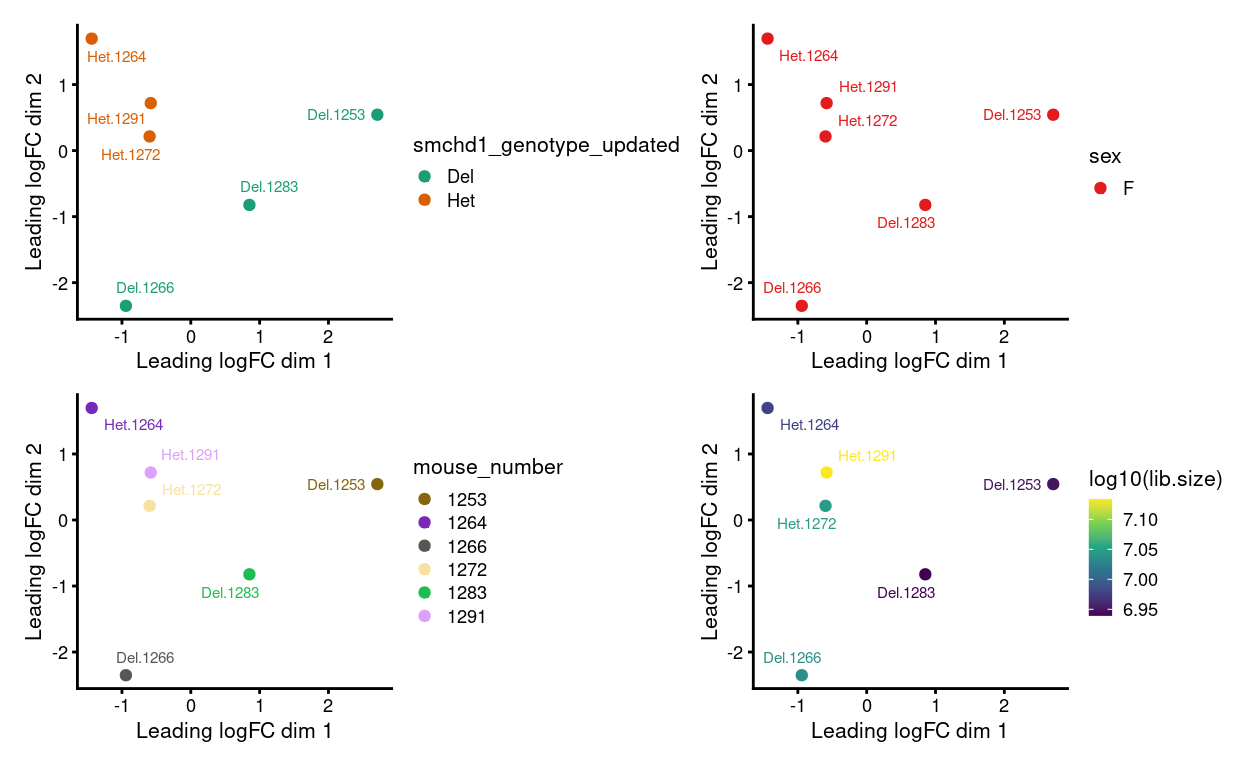
Figure 13: MDS plots of aggregated technical replicates following RUV coloured by various experimental factors.
DE analysis
Fit a model using edgeR with a term for smchd1_genotype_updated.
Show code
yf <- estimateDisp(yf, yf_design)
par(mfrow = c(1, 1))
plotBCV(yf)
Show code
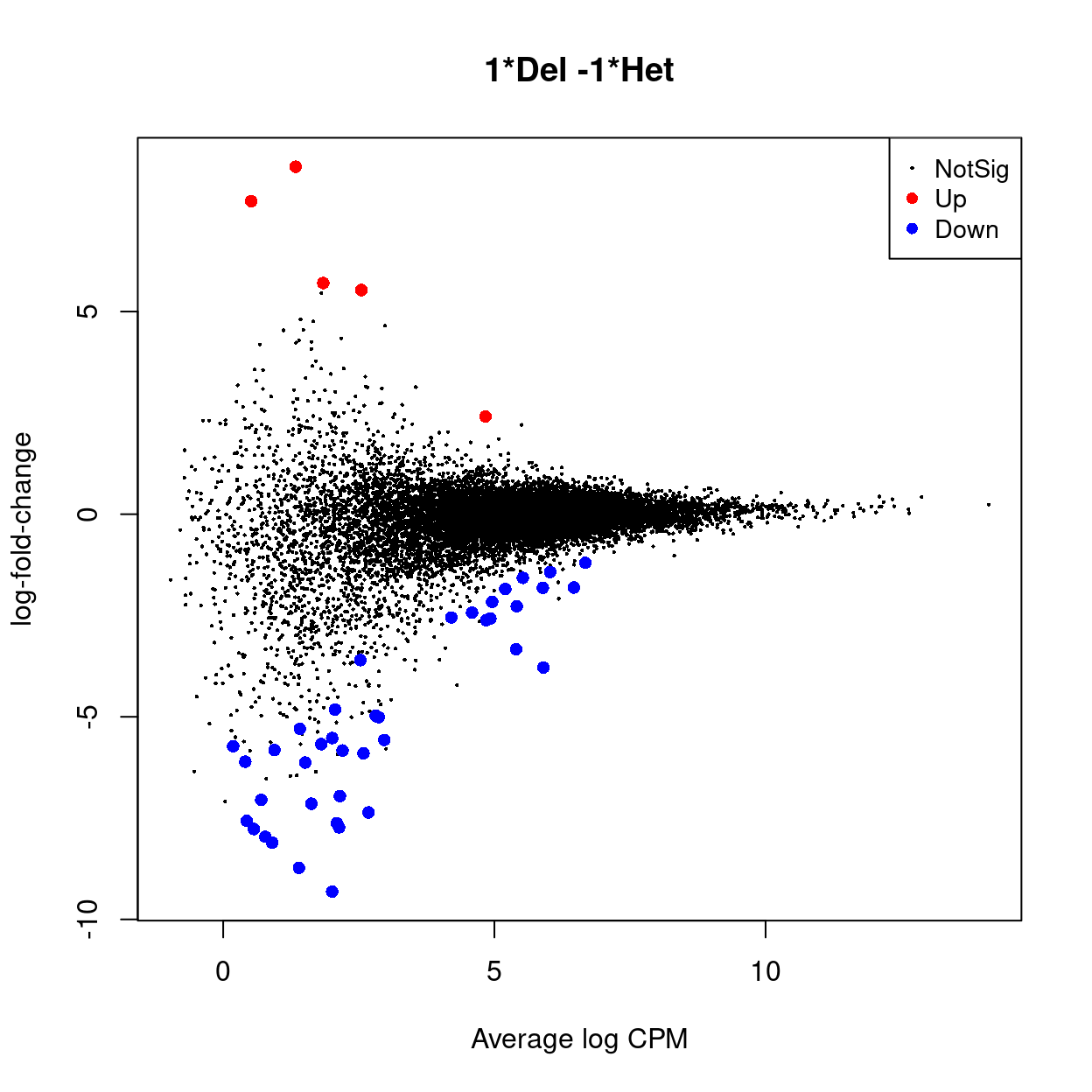
| 1Del -1Het | |
|---|---|
| Down | 40 |
| NotSig | 11468 |
| Up | 5 |
An interactive Glimma MD plot of the differential expression results is available from output/DEGs/reads/glimma-plots/aggregated_tech_reps.females.md-plot.html.
Show code
yf_tt <- topTags(yf_dgelrt, n = Inf, sort.by = "none")
glMDPlot(
x = yf_dgelrt,
counts = yf,
anno = yf$genes,
display.columns = c("ENSEMBL.SYMBOL"),
groups = yf$samples$group,
samples = colnames(yf),
status = yf_dt,
transform = TRUE,
sample.cols = yf$samples$smchd1_genotype_updated_colours,
path = outdir,
html = "aggregated_tech_reps.females.md-plot",
launch = FALSE)
CSV file of results available from output/DEGs/reads/aggregated_tech_reps.females.DEGs.csv.gz.
Show code
heatmapForPaper <- function() {
pheatmap(
cpm(yf, log = TRUE)[rownames(yf_tt), ],
cluster_rows = TRUE,
cluster_cols = FALSE,
color = hcl.colors(101, "Blue-Red 3"),
breaks = seq(-3, 3, length.out = 101),
scale = "row",
annotation_col = data.frame(
genotype = yf$samples$smchd1_genotype_updated,
sex = yf$samples$sex,
row.names = colnames(yf)),
annotation_colors = list(
genotype = smchd1_genotype_updated_colours,
sex = sex_colours),
main = "Female samples",
fontsize = 9)
}
Figure 15 is a heatmap showing the expression of the DEGs.
Show code
heatmapForPaper()
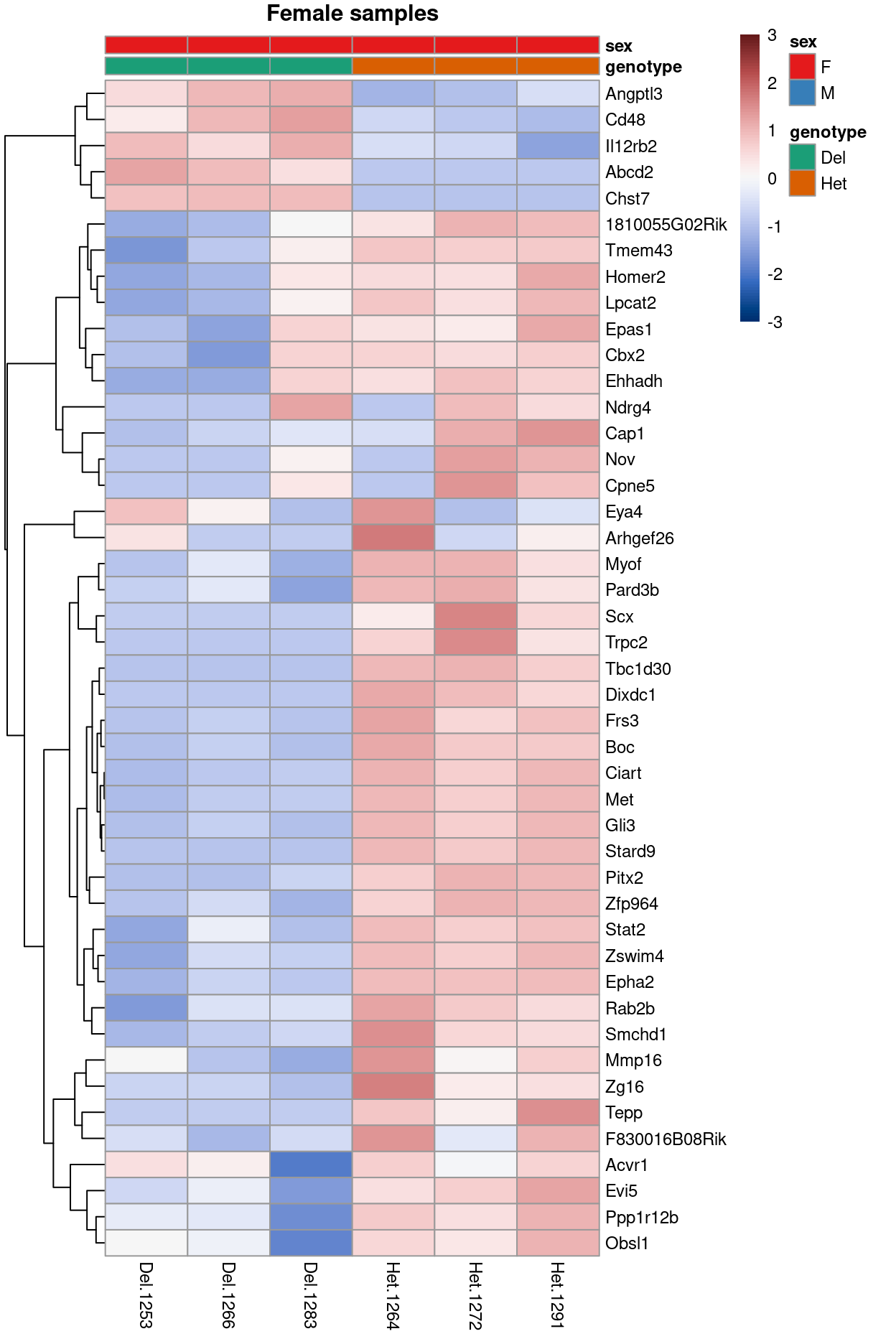
Figure 15: Heatmap of upper-quartile-normalzied logCPM values for the DEGs.
Gene set tests
Gene set testing is commonly used to interpret the differential expression results in a biological context. Here we apply various gene set tests to the DEG lists.
goana
We use the goana() function from the limma R/Bioconductor package to test for over-representation of gene ontology (GO) terms in each DEG list.
Show code
list_of_go <- lapply(colnames(yf_contrast), function(j) {
dgelrt <- glmLRT(yf_dgeglm, contrast = yf_contrast[, j])
go <- goana(
de = dgelrt,
geneid = sapply(strsplit(dgelrt$genes$NCBI.ENTREZID, "; "), "[[", 1),
species = "Mm")
gzout <- gzfile(
description = file.path(
outdir,
"aggregated_tech_reps.females.goana.csv.gz"),
open = "wb")
write.csv(
topGO(go, number = Inf),
gzout,
row.names = TRUE)
close(gzout)
go
})
names(list_of_go) <- colnames(yf_contrast)
CSV files of the results are available from output/DEGs/reads/.
An example of the results are shown below.
Show code
topGO(list_of_go[[1]]) %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = '`goana()` produces a table with a row for each GO term and the following columns: **Term** (GO term); **Ont** (ontology that the GO term belongs to. Possible values are "BP", "CC" and "MF"); **N** (number of genes in the GO term); **Up** (number of up-regulated differentially expressed genes); **Down** (number of down-regulated differentially expressed genes); **P.Up** (p-value for over-representation of GO term in up-regulated genes); **P.Down** (p-value for over-representation of GO term in down-regulated genes)')
| Term | Ont | N | Up | Down | P.Up | P.Down | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO:0009653 | anatomical structure morphogenesis | BP | 1565 | 1 | 19 | 0.5223220 | 0.0000003 |
| GO:0048562 | embryonic organ morphogenesis | BP | 156 | 0 | 6 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000156 |
| GO:0050996 | positive regulation of lipid catabolic process | BP | 15 | 2 | 0 | 0.0000161 | 1.0000000 |
| GO:0048754 | branching morphogenesis of an epithelial tube | BP | 93 | 0 | 5 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000171 |
| GO:0048568 | embryonic organ development | BP | 268 | 0 | 7 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000353 |
| GO:0035993 | deltoid tuberosity development | BP | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000360 |
| GO:0061138 | morphogenesis of a branching epithelium | BP | 110 | 0 | 5 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000385 |
| GO:0007166 | cell surface receptor signaling pathway | BP | 1413 | 1 | 15 | 0.4842227 | 0.0000454 |
| GO:0001763 | morphogenesis of a branching structure | BP | 118 | 0 | 5 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000539 |
| GO:0061061 | muscle structure development | BP | 393 | 0 | 8 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000544 |
| GO:0009887 | animal organ morphogenesis | BP | 533 | 0 | 9 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000746 |
| GO:0014902 | myotube differentiation | BP | 68 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0000902 |
| GO:0050994 | regulation of lipid catabolic process | BP | 35 | 2 | 0 | 0.0000911 | 1.0000000 |
| GO:0090596 | sensory organ morphogenesis | BP | 137 | 0 | 5 | 1.0000000 | 0.0001095 |
| GO:0048593 | camera-type eye morphogenesis | BP | 72 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0001128 |
| GO:0090630 | activation of GTPase activity | BP | 75 | 0 | 4 | 1.0000000 | 0.0001322 |
| GO:0019199 | transmembrane receptor protein kinase activity | MF | 30 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0001523 |
| GO:0048557 | embryonic digestive tract morphogenesis | BP | 6 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0001786 |
| GO:0003170 | heart valve development | BP | 32 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0001852 |
| GO:0001707 | mesoderm formation | BP | 33 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0002032 |
kegga
We use the kegga() function from the limma R/Bioconductor package to test for over-representation of KEGG pathways in each DEG list.
Show code
list_of_kegg <- lapply(colnames(yf_contrast), function(j) {
dgelrt <- glmLRT(yf_dgeglm, contrast = yf_contrast[, j])
kegg <- kegga(
de = dgelrt,
geneid = sapply(strsplit(dgelrt$genes$NCBI.ENTREZID, "; "), "[[", 1),
species = "Mm")
gzout <- gzfile(
description = file.path(
outdir,
"aggregated_tech_reps.females.kegga.csv.gz"),
open = "wb")
write.csv(
topKEGG(kegg, number = Inf),
gzout,
row.names = TRUE)
close(gzout)
kegg
})
names(list_of_kegg) <- colnames(yf_contrast)
CSV files of the results are available from output/DEGs/reads/.
An example of the results are shown below.
Show code
topKEGG(list_of_kegg[[1]]) %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = '`kegga()` produces a table with a row for each KEGG pathway ID and the following columns: **Pathway** (KEGG pathway); **N** (number of genes in the GO term); **Up** (number of up-regulated differentially expressed genes); **Down** (number of down-regulated differentially expressed genes); **P.Up** (p-value for over-representation of KEGG pathway in up-regulated genes); **P.Down** (p-value for over-representation of KEGG pathway in down-regulated genes)')
| Pathway | N | Up | Down | P.Up | P.Down | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| path:mmu04360 | Axon guidance | 109 | 0 | 3 | 1.0000000 | 0.0065037 |
| path:mmu00532 | Glycosaminoglycan biosynthesis - chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate | 15 | 1 | 0 | 0.0065651 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04340 | Hedgehog signaling pathway | 42 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0094658 |
| path:mmu02010 | ABC transporters | 25 | 1 | 0 | 0.0109226 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04979 | Cholesterol metabolism | 29 | 1 | 0 | 0.0126614 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04350 | TGF-beta signaling pathway | 55 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0158649 |
| path:mmu05321 | Inflammatory bowel disease | 38 | 1 | 0 | 0.0165646 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu05100 | Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | 61 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0192945 |
| path:mmu05211 | Renal cell carcinoma | 62 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0198939 |
| path:mmu04658 | Th1 and Th2 cell differentiation | 65 | 1 | 0 | 0.0282002 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04650 | Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity | 67 | 1 | 0 | 0.0290577 | 1.0000000 |
| path:mmu04146 | Peroxisome | 67 | 1 | 1 | 0.0290577 | 0.2104325 |
| path:mmu05200 | Pathways in cancer | 352 | 1 | 4 | 0.1452135 | 0.0341319 |
| path:mmu04630 | JAK-STAT signaling pathway | 94 | 1 | 1 | 0.0405748 | 0.2824260 |
| path:mmu04060 | Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | 96 | 1 | 1 | 0.0414235 | 0.2874965 |
| path:mmu00650 | Butanoate metabolism | 16 | 0 | 1 | 1.0000000 | 0.0547407 |
| path:mmu00410 | beta-Alanine metabolism | 20 | 0 | 1 | 1.0000000 | 0.0679626 |
| path:mmu00380 | Tryptophan metabolism | 21 | 0 | 1 | 1.0000000 | 0.0712398 |
| path:mmu04510 | Focal adhesion | 127 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0730508 |
| path:mmu05206 | MicroRNAs in cancer | 131 | 0 | 2 | 1.0000000 | 0.0770741 |
camera with MSigDB gene sets
We use the camera() function from the limma R/Bioconductor package to test whether a set of genes is highly ranked relative to other genes in terms of differential expression, accounting for inter-gene correlation. Specifically, we test using gene sets from MSigDB, namely:
- H: hallmark gene sets are coherently expressed signatures derived by aggregating many MSigDB gene sets to represent well-defined biological states or processes.
- C2: curated gene sets from online pathway databases, publications in PubMed, and knowledge of domain experts.
Show code
yf_idx <- ids2indices(
msigdb,
id = sapply(strsplit(yf$genes$NCBI.ENTREZID, "; "), "[[", 1))
list_of_camera <- lapply(colnames(yf_contrast), function(j) {
cam <- camera(
y = yf,
index = yf_idx,
design = yf_design,
contrast = yf_contrast[, j])
gzout <- gzfile(
description = file.path(
outdir,
"aggregated_tech_reps.females.camera.csv.gz"),
open = "wb")
write.csv(
cam,
gzout,
row.names = TRUE)
close(gzout)
cam
})
names(list_of_camera) <- colnames(yf_contrast)
CSV files of the results are available from output/DEGs/reads.
An example of the results are shown below.
Show code
head(list_of_camera[[1]]) %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = '`camera()` produces a table with a row for each gene set (prepended by which MSigDB collection it comes from) and the following columns: **NGenes** (number of genes in set); **Direction** (direction of change); **PValue** (two-tailed p-value); **FDR** (Benjamini and Hochberg FDR adjusted p-value).')
| NGenes | Direction | PValue | FDR | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2.KEGG_RIBOSOME | 102 | Up | 0 | 1.0e-07 |
| C2.REACTOME_EUKARYOTIC_TRANSLATION_ELONGATION | 107 | Up | 0 | 1.0e-07 |
| C2.REACTOME_RESPONSE_OF_EIF2AK4_GCN2_TO_AMINO_ACID_DEFICIENCY | 115 | Up | 0 | 9.0e-07 |
| C2.REACTOME_RESPIRATORY_ELECTRON_TRANSPORT_ATP_SYNTHESIS_BY_CHEMIOSMOTIC_COUPLING_AND_HEAT_PRODUCTION_BY_UNCOUPLING_PROTEINS | 121 | Up | 0 | 1.3e-06 |
| C2.REACTOME_EUKARYOTIC_TRANSLATION_INITIATION | 139 | Up | 0 | 1.3e-06 |
| C2.REACTOME_SRP_DEPENDENT_COTRANSLATIONAL_PROTEIN_TARGETING_TO_MEMBRANE | 130 | Up | 0 | 1.9e-06 |
Sarah’s gene lists
Show code
yf_X <- yf$genes$ENSEMBL.SEQNAME == "X"
yf_protocadherin <- grepl("Pcdh", rownames(yf))
yf_pw <- rownames(yf) %in% c("Ndn", "Mkrn3", "Peg12")
yf_male <- male_het_vs_del[
male_het_vs_del$FDR < 0.05,
c("ENSEMBL.SYMBOL", "logFC")]
yf_female <- male_het_vs_del[
female_het_vs_del$FDR < 0.05,
c("ENSEMBL.SYMBOL", "logFC")]
yf_sun <- sun_2014[, c("geneSymbol", "log2FC")]
yf_chambers <- chambers_2007[, c("Gene Symbol", "Fold Difference")]
yf_chambers$logFC <- log2(yf_chambers$`Fold Difference`)
yf_chambers$`Fold Difference` <- NULL
yf_chambers <- yf_chambers[!is.na(yf_chambers$`Gene Symbol`), ]
yf_chambers <- yf_chambers[!duplicated(yf_chambers$`Gene Symbol`), ]
yf_gazit <- gazit_2013[, c("Symbol"), drop = FALSE]
yf_gazit$Symbol <- paste(
substring(yf_gazit$Symbol, 1, 1),
tolower(substring(yf_gazit$Symbol, 2)),
sep = "")
yf_gazit$logFC <- 1
yf_chambers_gazit <- data.frame(
Symbol = c(yf_chambers$`Gene Symbol`, yf_gazit$Symbol),
logFC = c(yf_chambers$logFC, yf_gazit$logFC))
yf_chambers_gazit <- yf_chambers_gazit[!duplicated(yf_chambers_gazit$Symbol), ]
yf_venezia_proliferation <- rownames(yf) %in% venezia_proliferation$Gene.Symbol
yf_venezia_quiescence <- rownames(yf) %in% venezia_quiescence$Gene.Symbol
yf_index <- list(
`X-linked` = yf_X,
Protocadherin = yf_protocadherin,
`Prader-Willi` = yf_pw,
`Male: Het vs. Del` = yf_male,
`Female: Het vs. Del` = yf_female,
`Sun (2014)` = yf_sun,
`Chambers (2007)` = yf_chambers,
`Gazit (2013)` = yf_gazit,
`Chambers (2007) & Gazit (2013)` = yf_chambers_gazit,
`Proliferation Group Venezia (2004)` = yf_venezia_proliferation,
`Quiescence Group Venezia (2004)` = yf_venezia_quiescence)
Sarah requested testing a number of gene sets (see Gene sets).
We use the fry() function from the edgeR R/Bioconductor package to perform a self-contained gene set test against the null hypothesis that none of the genes in the set are differentially expressed.
Show code
fry(
yf,
index = yf_index,
design = yf_design,
contrast = yf_contrast,
sort = "none") %>%
knitr::kable(
caption = "Results of applying `fry()` to the RNA-seq differential expression results using the supplied gene sets. A significant 'Up' P-value means that the differential expression results found in the RNA-seq data are positively correlated with the expression signature from the corresponding gene set. Conversely, a significant 'Down' P-value means that the differential expression log-fold-changes are negatively correlated with the expression signature from the corresponding gene set. A significant 'Mixed' P-value means that the genes in the set tend to be differentially expressed without regard for direction.")
| NGenes | Direction | PValue | FDR | PValue.Mixed | FDR.Mixed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-linked | 385 | Down | 0.7932572 | 0.8725829 | 0.0009255 | 0.0101804 |
| Protocadherin | 6 | Up | 0.3450358 | 0.5421992 | 0.5544190 | 0.7140077 |
| Prader-Willi | 3 | Up | 0.5275007 | 0.7253135 | 0.8358759 | 0.8358759 |
| Male: Het vs. Del | 7 | Up | 0.6811221 | 0.8324826 | 0.6306529 | 0.7140077 |
| Female: Het vs. Del | 16 | Up | 0.9166151 | 0.9166151 | 0.6490979 | 0.7140077 |
| Sun (2014) | 1986 | Down | 0.1441139 | 0.2642088 | 0.0025603 | 0.0140817 |
| Chambers (2007) | 204 | Down | 0.0110643 | 0.0961422 | 0.0219285 | 0.0482426 |
| Gazit (2013) | 248 | Down | 0.0573814 | 0.1577988 | 0.0189400 | 0.0482426 |
| Chambers (2007) & Gazit (2013) | 399 | Down | 0.0174804 | 0.0961422 | 0.0210045 | 0.0482426 |
| Proliferation Group Venezia (2004) | 365 | Up | 0.0531114 | 0.1577988 | 0.0462182 | 0.0847334 |
| Quiescence Group Venezia (2004) | 381 | Down | 0.0727634 | 0.1600795 | 0.1389243 | 0.2183096 |
Show code
geneSetTestFiguresForPaper <- function() {
for (n in names(yf_index)) {
if (is.data.frame(yf_index[[n]])) {
yf_status <- rep(0, nrow(yf_dgelrt))
yf_status[rownames(yf) %in% yf_index[[n]][, 1]] <-
sign(yf_index[[n]][yf_index[[n]][, 1] %in% rownames(yf), 2])
plotMD(
yf_dgelrt,
status = yf_status,
hl.col = c("red", "blue"),
legend = "bottomright",
main = n)
abline(h = 0, col = "darkgrey")
} else {
yf_status <- rep("Other", nrow(yf_dgelrt))
yf_status[yf_index[[n]]] <- n
plotMD(
yf_dgelrt,
status = yf_status,
values = n,
hl.col = "red",
legend = "bottomright",
main = n)
abline(h = 0, col = "darkgrey")
}
if (is.data.frame(yf_index[[n]])) {
barcodeplot(
yf_dgelrt$table$logFC,
rownames(yf) %in% yf_index[[n]][, 1],
gene.weights = yf_index[[n]][
yf_index[[n]][, 1] %in% rownames(yf), 2],
main = n)
} else {
barcodeplot(
yf_dgelrt$table$logFC,
yf_index[[n]],
main = n)
}
}
}
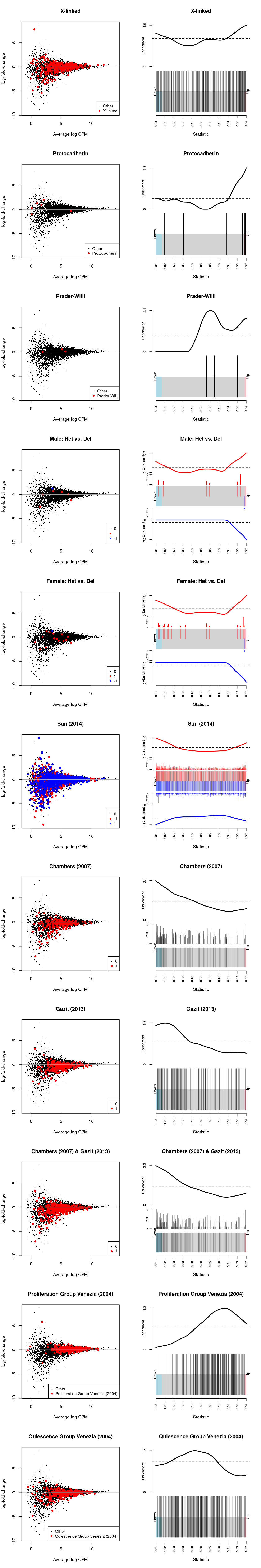
Figure 16: MD-plot and barcode plot of genes in supplied gene sets. Directional gene sets have (1) MD plot points coloured according to the statistical significance of the gene in the gene set (2) barcode plot ‘weights’ given by the logFC of the gene in the gene set. For the barcode plot, genes are represented by bars and are ranked from left to right by increasing log-fold change. This forms the barcode-like pattern. The line (or worm) above the barcode shows the relative local enrichment of the vertical bars in each part of the plot. The dotted horizontal line indicates neutral enrichment; the worm above the dotted line shows enrichment while the worm below the dotted line shows depletion.
Session info
Show code
sessioninfo::session_info()
─ Session info ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────
setting value
version R version 4.0.3 (2020-10-10)
os CentOS Linux 7 (Core)
system x86_64, linux-gnu
ui X11
language (EN)
collate en_US.UTF-8
ctype en_US.UTF-8
tz Australia/Melbourne
date 2021-10-20
─ Packages ─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
! package * version date lib source
P annotate 1.68.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P AnnotationDbi 1.52.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P aroma.light 3.20.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P askpass 1.1 2019-01-13 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P assertthat 0.2.1 2019-03-21 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P Biobase * 2.50.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P BiocFileCache * 1.14.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P BiocGenerics * 0.36.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P BiocManager 1.30.10 2019-11-16 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P BiocParallel * 1.24.1 2020-11-06 [?] Bioconductor
P BiocStyle 2.18.1 2020-11-24 [?] Bioconductor
P biomaRt 2.46.3 2021-02-09 [?] Bioconductor
P Biostrings * 2.58.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P bit 4.0.4 2020-08-04 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P bit64 4.0.5 2020-08-30 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P bitops 1.0-6 2013-08-17 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P blob 1.2.1 2020-01-20 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P cachem 1.0.4 2021-02-13 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P cellranger 1.1.0 2016-07-27 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P cli 2.3.1 2021-02-23 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P colorspace 2.0-0 2020-11-11 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P cowplot * 1.1.1 2020-12-30 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P crayon 1.4.1 2021-02-08 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P crosstalk 1.1.1 2021-01-12 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P curl 4.3 2019-12-02 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P data.table 1.14.0 2021-02-21 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P DBI 1.1.1 2021-01-15 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P dbplyr * 2.1.0 2021-02-03 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P DelayedArray 0.16.1 2021-01-22 [?] Bioconductor
P DESeq2 1.30.1 2021-02-19 [?] Bioconductor
P digest 0.6.27 2020-10-24 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.2)
P distill 1.2 2021-01-13 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P downlit 0.2.1 2020-11-04 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P dplyr 1.0.4 2021-02-02 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P DT 0.17 2021-01-06 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P EDASeq * 2.24.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P edgeR * 3.32.1 2021-01-14 [?] Bioconductor
P ellipsis 0.3.1 2020-05-15 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P evaluate 0.14 2019-05-28 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P fansi 0.4.2 2021-01-15 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P farver 2.0.3 2020-01-16 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P fastmap 1.1.0 2021-01-25 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P genefilter 1.72.1 2021-01-21 [?] Bioconductor
P geneplotter 1.68.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P generics 0.1.0 2020-10-31 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P GenomeInfoDb * 1.26.2 2020-12-08 [?] Bioconductor
P GenomeInfoDbData 1.2.4 2020-10-20 [?] Bioconductor
P GenomicAlignments * 1.26.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P GenomicFeatures 1.42.1 2020-11-12 [?] Bioconductor
P GenomicRanges * 1.42.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P ggplot2 * 3.3.3 2020-12-30 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P ggrepel * 0.9.1 2021-01-15 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P Glimma * 2.0.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P glue 1.4.2 2020-08-27 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P GO.db 3.12.1 2020-11-04 [?] Bioconductor
P gtable 0.3.0 2019-03-25 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P here * 1.0.1 2020-12-13 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P highr 0.8 2019-03-20 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P hms 1.0.0 2021-01-13 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P htmltools 0.5.1.1 2021-01-22 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P htmlwidgets 1.5.3 2020-12-10 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P httr 1.4.2 2020-07-20 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P hwriter 1.3.2 2014-09-10 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P IRanges * 2.24.1 2020-12-12 [?] Bioconductor
P jpeg 0.1-8.1 2019-10-24 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P jsonlite 1.7.2 2020-12-09 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P knitr 1.31 2021-01-27 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P labeling 0.4.2 2020-10-20 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P lattice 0.20-41 2020-04-02 [3] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P latticeExtra 0.6-29 2019-12-19 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P lifecycle 1.0.0 2021-02-15 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P limma * 3.46.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P locfit 1.5-9.4 2020-03-25 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P magrittr * 2.0.1 2020-11-17 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P MASS 7.3-53 2020-09-09 [3] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P Matrix 1.2-18 2019-11-27 [3] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P MatrixGenerics * 1.2.1 2021-01-30 [?] Bioconductor
P matrixStats * 0.58.0 2021-01-29 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P memoise 2.0.0 2021-01-26 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P munsell 0.5.0 2018-06-12 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P openssl 1.4.3 2020-09-18 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.2)
P org.Mm.eg.db 3.12.0 2020-10-20 [?] Bioconductor
P patchwork * 1.1.1 2020-12-17 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P pheatmap * 1.0.12 2019-01-04 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P pillar 1.5.0 2021-02-22 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P pkgconfig 2.0.3 2019-09-22 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P png 0.1-7 2013-12-03 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P prettyunits 1.1.1 2020-01-24 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P progress 1.2.2 2019-05-16 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P purrr 0.3.4 2020-04-17 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P R.methodsS3 1.8.1 2020-08-26 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P R.oo 1.24.0 2020-08-26 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P R.utils 2.10.1 2020-08-26 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P R6 2.5.0 2020-10-28 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.2)
P rappdirs 0.3.3 2021-01-31 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P RColorBrewer 1.1-2 2014-12-07 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P Rcpp 1.0.6 2021-01-15 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P RCurl 1.98-1.2 2020-04-18 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P readxl * 1.3.1 2019-03-13 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P rematch 1.0.1 2016-04-21 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P rlang 0.4.10 2020-12-30 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P rmarkdown 2.11 2021-09-14 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P rprojroot 2.0.2 2020-11-15 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P Rsamtools * 2.6.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P RSQLite 2.2.3 2021-01-24 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P rtracklayer 1.50.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P RUVSeq * 1.24.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P S4Vectors * 0.28.1 2020-12-09 [?] Bioconductor
P scales 1.1.1 2020-05-11 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P sessioninfo 1.1.1 2018-11-05 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P ShortRead * 1.48.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P SingleCellExperiment * 1.12.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P stringi 1.5.3 2020-09-09 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P stringr 1.4.0 2019-02-10 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P SummarizedExperiment * 1.20.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P survival 3.2-7 2020-09-28 [3] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P tibble 3.0.6 2021-01-29 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P tidyselect 1.1.0 2020-05-11 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P utf8 1.1.4 2018-05-24 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P vctrs 0.3.6 2020-12-17 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P viridisLite 0.3.0 2018-02-01 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P withr 2.4.1 2021-01-26 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.3)
P xfun 0.26 2021-09-14 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P XML 3.99-0.5 2020-07-23 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P xml2 1.3.2 2020-04-23 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P xtable 1.8-4 2019-04-21 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P XVector * 0.30.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
P yaml 2.2.1 2020-02-01 [?] CRAN (R 4.0.0)
P zlibbioc 1.36.0 2020-10-27 [?] Bioconductor
[1] /stornext/Projects/score/Analyses/C086_Kinkel/renv/library/R-4.0/x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
[2] /tmp/RtmpfgojZ6/renv-system-library
[3] /stornext/System/data/apps/R/R-4.0.3/lib64/R/library
P ── Loaded and on-disk path mismatch.Details of RUVs parameters are given separately for each analysis.↩︎
see [
docs/C086_Kinkel.male_B_cells.multi-sample_comparisons.html(../docs/C086_Kinkel.male_B_cells.multi-sample_comparisons.html)]↩︎see [
docs/C086_Kinkel.female_B_cells.multi-sample_comparisons.html(../docs/C086_Kinkel.female_B_cells.multi-sample_comparisons.html)]↩︎My understanding of this terms translates as ‘upregulated DEGs.’↩︎